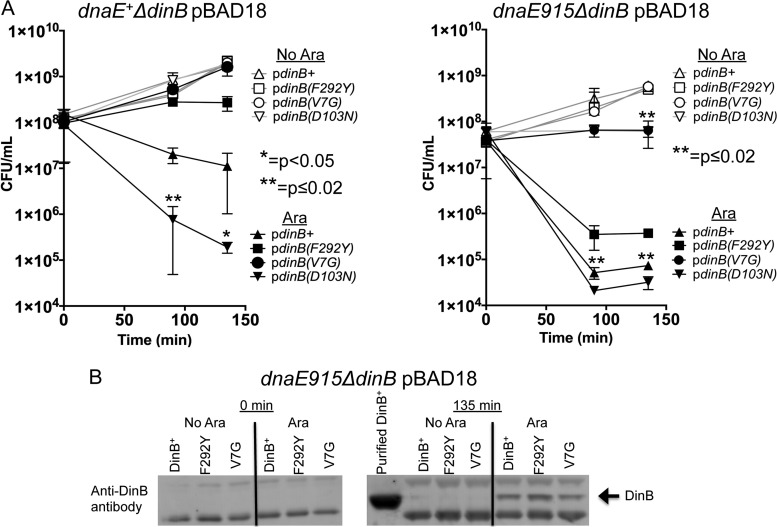
FIG 6.
The dinB(F292Y) and dinB(V7G) alleles also suppress DinB-mediated overexpression toxicity in dnaE+ cells. (A) Samples were collected at the indicated times from cultures with (filled symbols) or without (empty symbols) arabinose induction. Overproduction of wild-type DinB (filled triangle) or catalytically inactive DinB(D103N) (filled inverted triangle) is toxic to both dnaE+ and dnaE915 strains. The DinB(F292Y) (squares) and DinB(V7G) (circles) variants suppress DinB-mediated toxicity, compared to DinB (triangles) in both dnaE+ and dnaE915 strains. Error bars represent the standard deviations of the means from at least 3 independent isolates. (B) dnaE915 strains overexpress DinB, DinB(F292Y), or DinB(V7G) at similar levels. Immunoblotting (as described in Materials and Methods) assessed whether DinB and DinB(F292Y) or DinB(V7G) are equally translated. In uninduced cultures, DinB and its variants are undetectable. Purified DinB protein (750 ng) was used for sizing purposes. Samples were loaded with comparable protein concentrations as shown by cross-reactive bands.