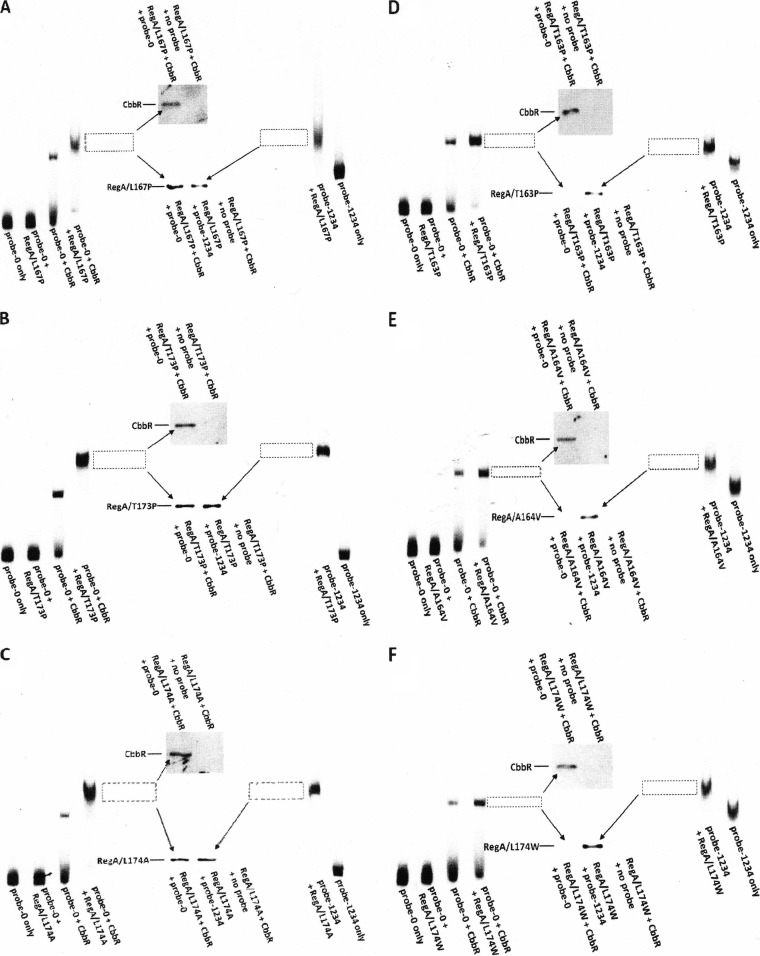
FIG 4.
A combination of immunoblot and gel mobility shift analyses illustrates the presence of mutant RegA and CbbR proteins extracted from CbbR/RegA/cbb promoter complexes. Proteins from protein/DNA complexes contained in-gel fragments (represented by dashed boxes) excised from nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels that were extracted, isolated, and subjected to immunoblotting as described in Materials and Methods. Gel mobility shifts are shown on the far left and far right of each individual panel (A to F), and immunoblots (detecting mutant RegA and CbbR) are located in the center. Polyclonal antibodies generated against RegA from R. sphaeroides were used to identify and detect the presence of the RegA mutant proteins; a monoclonal antibody generated against His-tagged proteins identified and detected the presence of His-tagged CbbR (see Materials and Methods). Every lane from the gel mobility shifts and immunoblots was identified with respect to the protein(s) and cbb probe DNA in each reaction. A control using probe-1234 was run for each mutant RegA protein (to the right in panels A to F) to verify that the antibodies would detect mutant RegA proteins, thus validating the results obtained with RegA/CbbR/cbbI promoter complexes (to the left in panels A to F). The RegA mutants used in this study were as follows: RegAL167P (A); RegAT173P (B); RegAL174A (C); RegAT163P (D); RegAA164V (E); RegAL174W (F).