FIG 2.
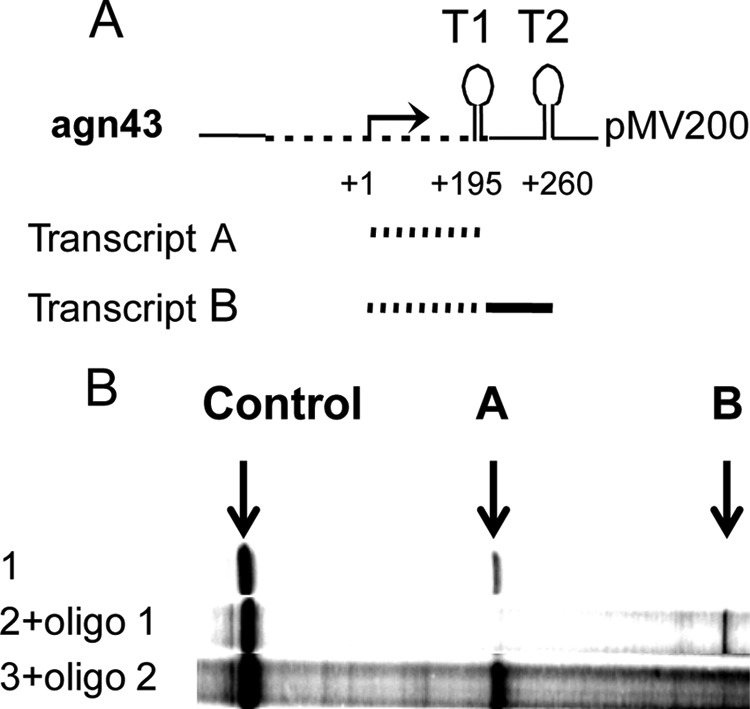
The agnK12 leader RNA features a transcription terminator functional in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of part of plasmid pMV201, containing agnK12 from positions −466 to +198. The dashed lines represent the agnK12 sequence, and the solid lines represent the vector sequence. The agnK12 transcription start is indicated (+1), and in the top cartoon, T1 and T2 refer to the terminator in agnK12 and the vector sequence, respectively. (B) Results from an in vitro transcription assay using pMV201 as a template in the absence (lane 1) and presence (lane 2) of a 100× molar excess of an oligomer hybridizing to the agnK12 sequence spanning positions +162 to +173 (see Materials and Methods), which competes with stem formation in T1. Lane 3 shows the lack of an effect of a control oligomer hybridizing to the agnK12 sequence spanning positions +44 to +56. The bands representing the 195-nt RNA terminating at T1 (A) and the approximately 260-nt RNA terminating at T2 (B) are indicated. An RNA transcribed from the vector (“Control”) is shown, as it serves as a loading control. Migration on the gel is from right to left.
