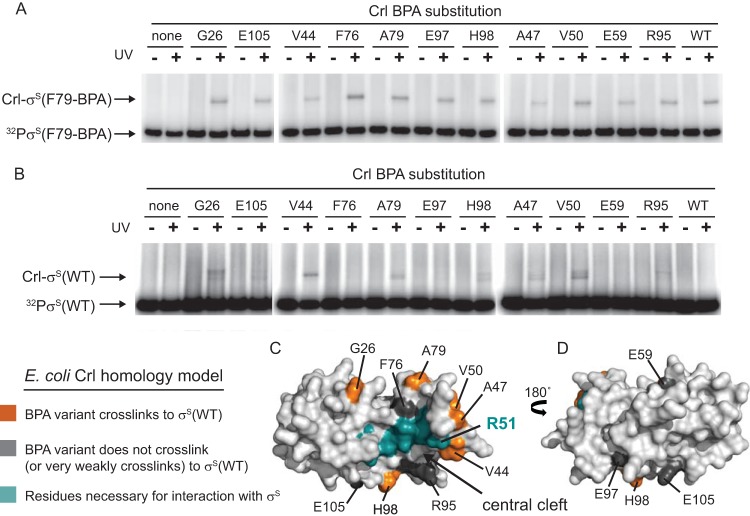
FIG 6.
BPA-mediated cross-linking of Crl to σS. (A and B) SDS-PAGE gels showing the results of UV exposure on 32P-σS(F79BPA) (A) or 32P-σS(WT) (B) incubated with either WT Crl or Crl variants with the photoreactive amino acid analog BPA incorporated at the indicated positions. Free 32P-σS and cross-linked 32P-σS-Crl complexes are indicated with arrows. Crl-BPA variants did not produce higher-molecular-weight bands in the absence of UV treatment or without σS. (C and D) Surface representations of the E. coli Crl homology model. Panel D is a 180° rotation of panel C. The positions of BPA substitutions in panels A and B are labeled and colored: orange, Crl-BPA variants that cross-link strongly to σS(WT); dark gray, Crl-BPA variants that cross-link very weakly or not at all to σS(WT); teal, residues in the central cleft patch proposed to interact with σS (Fig. 3B shows the identities of residues in addition to R51).