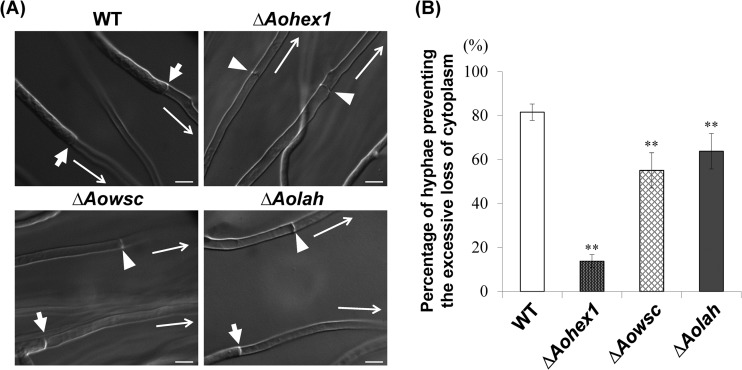
FIG 3.
Ability of Aolah disruptant cells to prevent excessive loss of cytoplasm upon hyphal wounding. (A) Differential interference contrast images of wounded hyphae capable or incapable of preventing the excessive loss of cytoplasm from the second cell upon hyphal tip bursting. A colony grown on agar medium was subjected to hypotonic shock by flooding with water to induce hyphal tip bursting, and the first septum adjacent to the burst tip cell was observed by differential interference contrast microscopy. Arrows indicate the first septa in the hyphae preventing the excessive loss of cytoplasm, and arrowheads show the septa in the hyphae not preventing excessive cytoplasmic loss. Long arrows indicate the directions toward the burst hyphal tips. Bars, 10 μm. (B) Assay of the ability of cells to prevent excessive loss of cytoplasm upon hyphal wounding. The wild-type (WT) strain and Aohex1, Aowsc, and Aolah gene disruptant strains were subjected to hypotonic shock, and hyphae with cells adjacent to the burst tip cell that retained the cytoplasm were counted by differential interference contrast microscopy. Average percentages of hyphae preventing the excessive loss of cytoplasm are shown in the graph. Fifty randomly selected hyphae with burst hyphal tips were observed for each culture. The error bars indicate standard deviations. **, P < 0.01 (by one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett's post hoc test for comparison with the wild-type strain; n = 9).