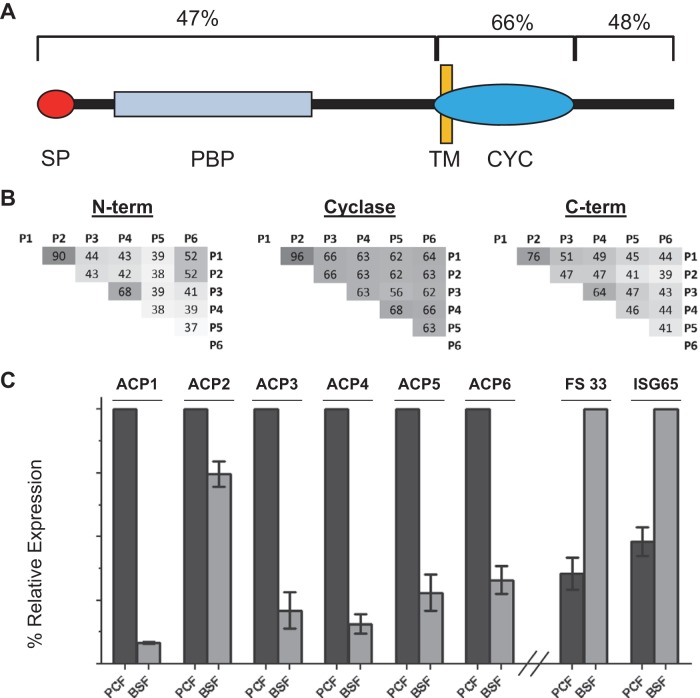
FIG 1.
Procyclic stage-specific receptor adenylate cyclases. (A) The schematic shows the general architecture of T. brucei adenylate cyclases, including a signal peptide (SP), a single-pass transmembrane domain (TM), and a cyclase catalytic domain (CYC), followed by a short intracellular C-terminal region. Within the N-terminal region are one to two domains homologous to periplasmic binding proteins (PBPs) of bacteria. The average sequence identity among ACP1 to ACP6 is shown above each section. (B) Pairwise amino acid sequence identities within the N-terminal, catalytic, and C-terminal domains of ACP1 to ACP6 (P1 to P6). (C) The chart shows the relative mRNA abundance in procyclic culture-form (PCF) and bloodstream-form (BSF) cells for the genes for adenylate cyclases ACP1 to ACP6 and FS33, as determined by qRT-PCR. ISG65 is a bloodstream-form-enriched gene (90) used as a control. The expression levels for each gene are normalized to the levels for the life cycle stage expressing the genes at higher levels.