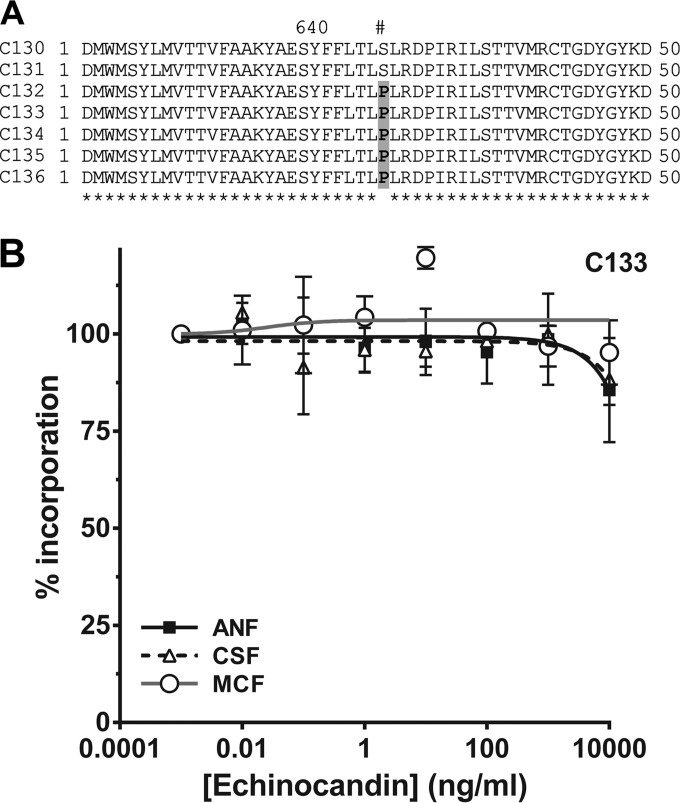
FIG 5.
Molecular and biochemical analysis of the CkFKS1 and GS complex from a series of isolates recovered from a single patient. (A) DNA sequence analysis of HS1 of isolates C130 to C136. RES isolates C132 to C136 harbor the most common amino acid substitution within HS1 leading to echinocandin resistance (S645P; shaded in gray). Amino acid residue numbers (above) are relative to the C. albicans Fks1p (Gsc1p/Orf19.2929p) (Candida Genome Database, http://www.candidagenome.org/). (B) Echinocandin inhibition assay of the enriched GS complex isolated from the representative isolate C133. The incorporation of [3H]glucose into the polymerized product was measured as a function of the echinocandin concentration. The GS complex from this isolate was insensitive to all three echinocandins up to 10,000 ng/ml. Error bars represent standard errors of the means (SEM).