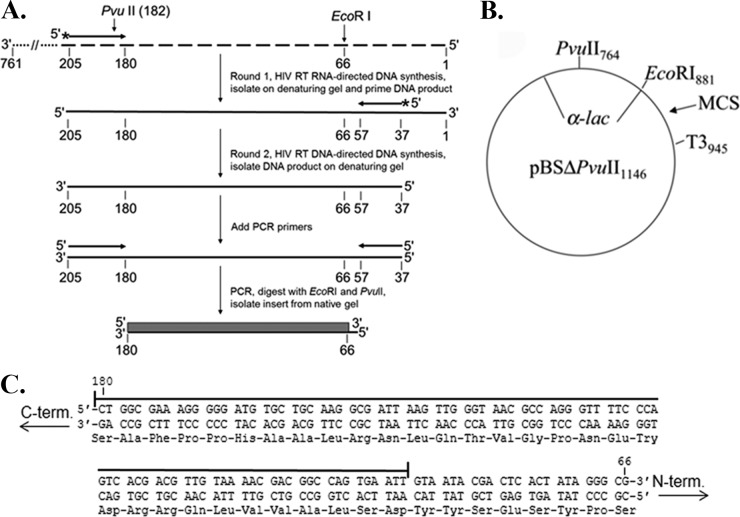
FIG 1.
PCR-based lacZα complementation system used to determine the fidelity of HIV RT. (A) An overview of the procedure used to assess polymerase fidelity is presented. RNAs are indicated by broken lines and DNAs by solid lines. Primers have arrowheads at the 3′ end. The ∼760-nucleotide template RNA used as the initial template for HIV RT RNA-directed DNA synthesis is shown at the top with the 3′ and 5′ ends indicated. The positions of PvuII and EcoRI restriction sites are indicated for reference to the vector. The filled box at the bottom of is the 115-base region of the lacZα gene that was scored in the assay. Details for specific steps are provided in Materials and Methods. (B) Plasmid pBSM13ΔPvuII1146 is shown. Relevant sites on the plasmid are indicated; numbering is based on that for the parent plasmid (pBSM13+ [Stratagene]). (C) The nucleotide and amino acid sequences for the 115-base region of the lacZα gene that was scored in the assay are shown. Both strands of the DNA plasmid are shown since HIV RT synthesis was performed in both directions (see panel A). A line is drawn above the 92 nt that are in the detectable area for substitution mutations, while frameshifts can be detected over the entire 115-nucleotide region. Based on a previous cataloging of mutations in this gene (19), the assay can detect 116 different substitutions (33.6% of the 345 possible substitutions in the 115-nucleotide sequence) and 100% of the frameshift mutations.