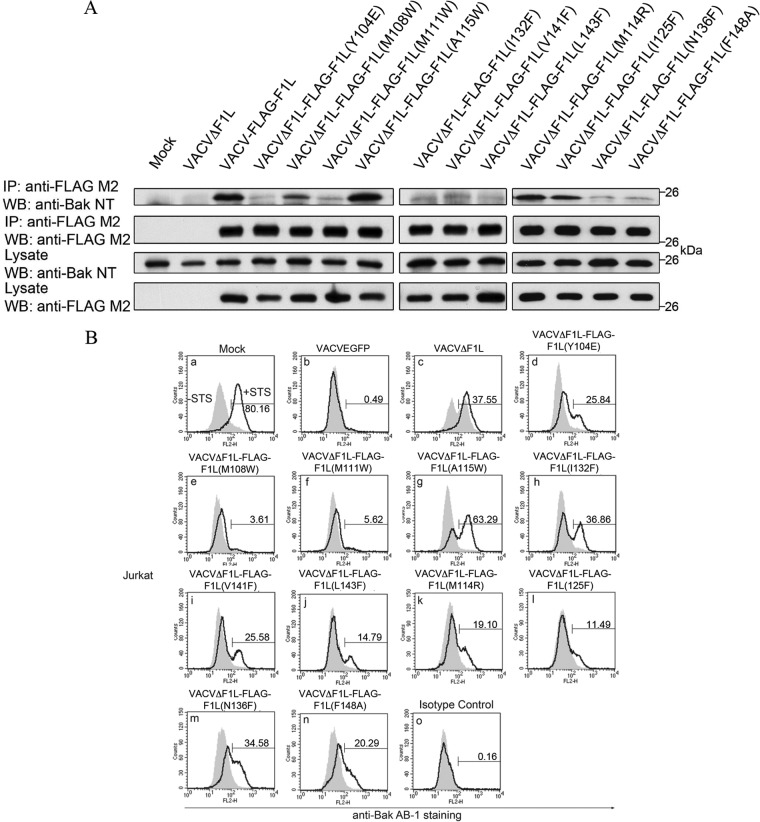
FIG 4.
F1L binding pocket residues are responsible for Bak interaction and prevention of Bak activation. (A) HeLa cells were mock infected or infected with VACVΔF1L, VACV-FLAG-F1L, or recombinant virus expressing the F1L binding pocket mutations. Infected-cell lysates were then immunoprecipitated (IP) with a monoclonal antibody recognizing FLAG, and Bak was detected by blotting with an anti-Bak monoclonal antibody (40, 41). (B) Jurkat cells were infected with WT VACV expressing EGFP, VACVΔF1L, or a panel of recombinant VACVs carrying F1L point mutations (VACVΔF1L-F1L) for 4 h at an MOI of 10 before treatment with 250 nM STS for 1.5 h to induce apoptosis. Bak N-terminal exposure was monitored by staining cells with the conformation-specific anti-Bak AB-1 antibody (40, 41) or an anti-NK1.1 antibody (42) as an isotype control. Shaded histograms, untreated cells; open histograms, STS-treated cells. WB, Western blotting.