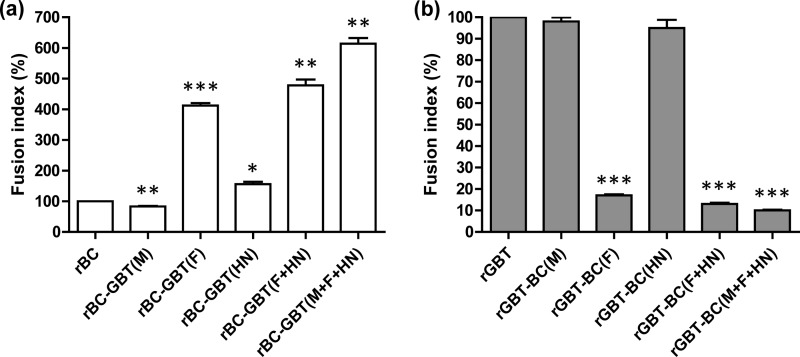
FIG 4.
Comparison of the fusion indices of parental rBC and rGBT and their chimeric derivatives involving the envelope-associated protein genes. Vero cells were infected with each virus at an MOI of 0.1, fixed at 36 h postinfection, and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. The fusion index was calculated as the ratio of the total number of nuclei to the total number of nuclei in the field, normalized to the respective parental virus, as 100. Data represent the means of the results from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate test of significance of the fusion index of a chimeric virus compared to the parental virus of that group; P values were calculated based on a two-tailed, unpaired t test (95% confidence levels). ***, P = 0.0001 to 0.001, extremely significant; **, P = 0.001 to 0.01, very significant; *, P = 0.01 to 0.05, significant.