FIG 1.
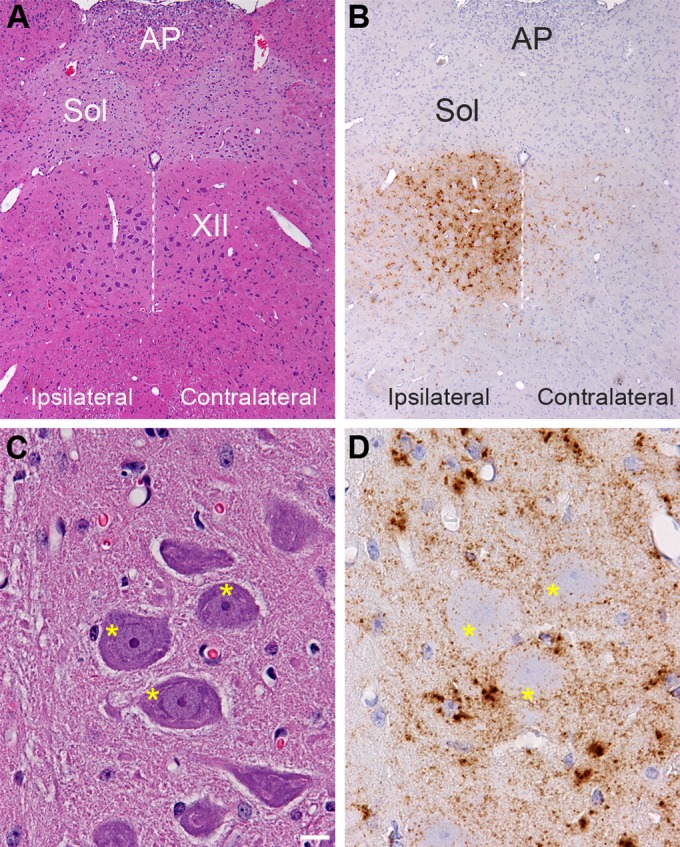
Distribution of PrPSc in the hypoglossal nucleus following HY TME infection. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of brain stem (A and C) and PrPSc immunohistochemistry (B and D) in adjacent tissue sections revealed a strong PrPSc pattern (brown) in the hypoglossal nucleus (XII) at 28 days postinoculation. PrPSc deposition was more intense ipsilateral to the inoculation site in the hypoglossal nerve than in the contralateral CN XII. Panels in C and D are higher magnifications of the ipsilateral CN XII illustrated in panels A and B. The dotted white line is located along the midline below the third ventricle, and it bisects CN XII. Higher magnification of ipsilateral CN XII is annotated with asterisks, which are located on the somata of hypoglossal motor neurons. This illustrates PrPSc deposition primarily at the edge of the neuronal soma and weakly within the soma. The PrPSc deposition pattern is also consistent with deposition in the neuropil or dendrites around the somata of motor neurons, and the dense clusters of PrPSc are likely to be associated with glial cells adjacent to motor neurons in CN XII. PrPSc immunohistochemistry was counterstained with hematoxylin. AP, area postremus; Sol, nucleus of the solitary tract. Scale bar, 10 μm.
