FIG 6.
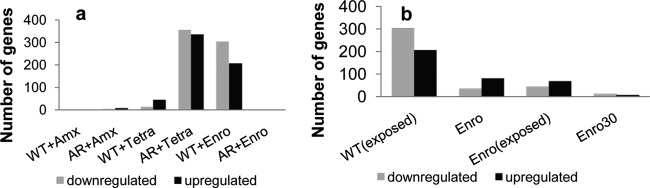
Change in transcriptomic profile of wild-type and antibiotic-resistant E. coli cells in response to short-term (<10 generations) drug exposure and long-term adaptation (>100 generations). (a) Number of up- and downregulated genes after antibiotic exposure (0.25× MIC, 1 μg/ml amoxicillin, 0.25 μg/ml tetracycline, and 0.125 μg/ml enrofloxacin) in wild-type (WT) and antibiotic-resistant (AR) cells compared to wild-type cells. (b) Number of up- or downregulated genes in AR cells compared to wild-type cells for the wild-type cells exposed to 0.25× MIC enrofloxacin [WT(exposed)], enrofloxacin-adapted cells (Enro), enrofloxacin-adapted cells exposed to 0.25× MIC [Enro(exposed)], and enrofloxacin-adapted cells cultured for 30 days without the antibiotic (Enro 30).
