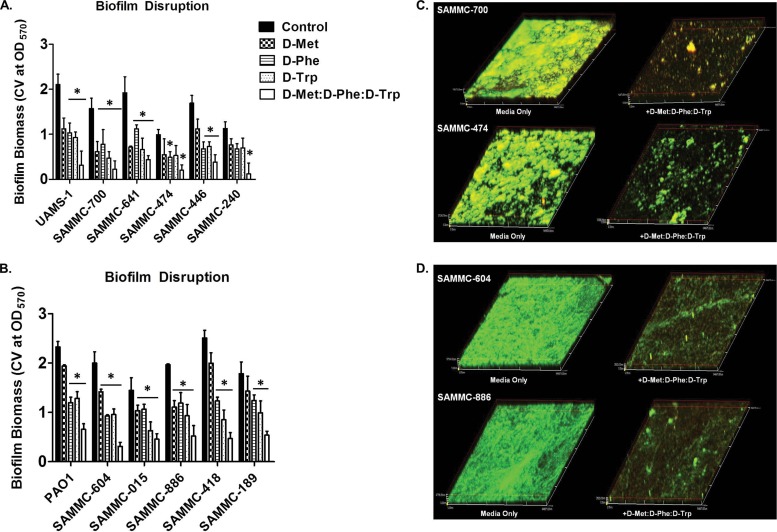
FIG 2.
Biofilm dispersive activity of d-AAs on clinical wound isolates. Activity of d-AAs d-Met, d-Phe, and d-Trp individually at 5 mM and as an equimolar mixture (1:1:1 d-Met/d-Phe/d-Trp) against biofilms of methicillin-resistant (SAMMC-700, SAMMC-641, SAMMC-474, SAMMC-446 and SAMMC-240) and methicillin-susceptible (UAMS-1) S. aureus isolates (A) and multidrug-resistant (SAMMC-604, SAMMC-015, SAMMC-886, SAMMC-418, and SAMMC-189) strains of P. aeruginosa (B). Biofilm dispersal was assessed by measuring the absorbance of solubilized crystal violet from stained biofilms following treatment with d-AA at 570 nm. *, P < 0.05 versus untreated control. Representative CLSM images of biofilms of (C) S. aureus and (D) P. aeruginosa clinical isolates treated with an equimolar mixture of d-AAs for 24 h. Biofilms were stained with dual combinations of biofilm ruby matrix stain (red) and biofilm cell stain (green) and images were taken at a magnification of ×20.