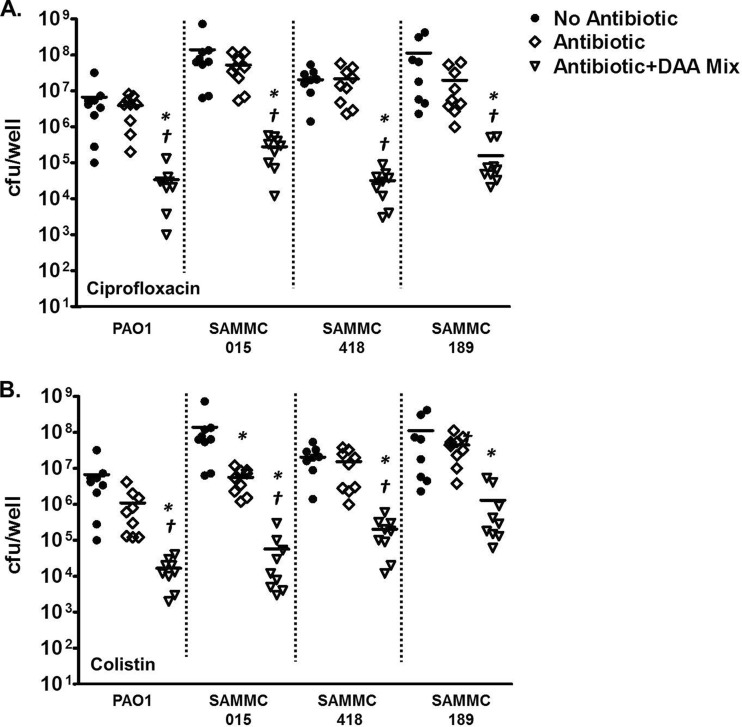
FIG 4.
Effect of combinations of d-AAs and antibiotics against biofilms of clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa. Biofilms of multidrug-resistant clinical strains (SAMMC-015, SAMMC-418, and SAMMC-189) and a laboratory strain (PAO1) of P. aeruginosa were developed on pegs of MBEC-HTP plates (Innovotech) for 24 h, followed by exposure to ciprofloxacin (32 μg/ml) (A) or colistin (64 μg/ml) (B) in the absence (◇) or presence of the d-AA mixture (1:1:1 d-Met/d-Phe/d-Trp) (▽) for 24 h. Viable bacteria from biofilms were determined by plating serial dilutions, following removal of adherent bacteria by sonication. Values are expressed as log10 (CFU/well). *, P < 0.05 versus control; †, P < 0.05 versus antibiotic alone.