FIG 1.
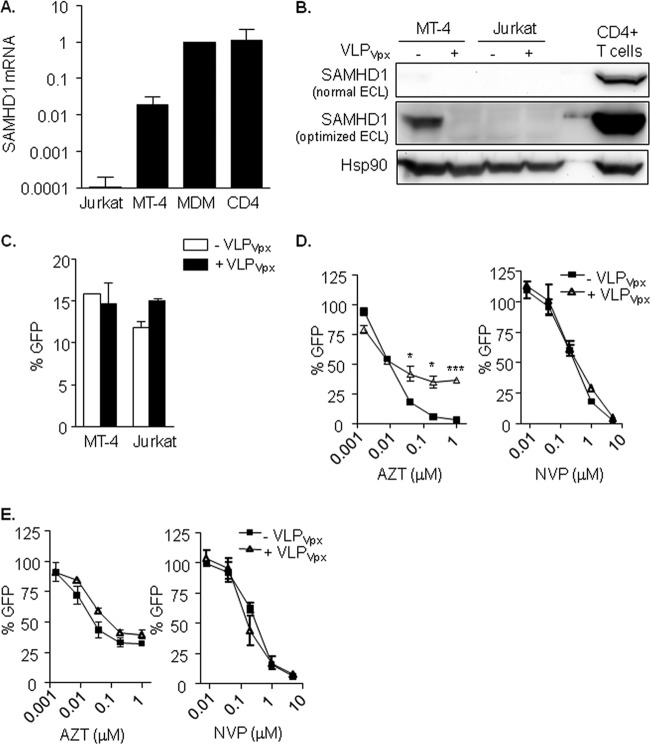
(A) SAMHD1 mRNA expression in T cell lines and primary cells. Relative mRNA expression of the SAMHD1 gene showing the diverse expression levels depending on cell type. (B) SAMHD1 protein expression and degradation by VLPVpx in T cell lines. Western blot of SAMHD1 expression in MT-4 and Jurkat T cell lines treated or not with VLPVpx for 24 h. Activated CD4+ T cells are included as a reference to illustrate the different degree of expression. SAMHD1 protein was detected only in MT-4 cells and after optimizing band detection by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL). (C) HIV-1 replication is not affected by Vpx in MT-4 and Jurkat T cell lines. Percentage of infected cells after treatment with VLPVpx. Cells were transduced with VLP carrying HIV-2 Vpx or left untreated for 4 h and then infected with a VSV-pseudotyped HIV-1 GFP-expressing virus. After 48 h, infection was assessed by flow cytometry. (D and E) Absence of SAMHD1 affects AZT antiviral potency in T cell lines. Dose response of AZT and NVP in MT-4 (D) and Jurkat (E) T cell lines treated or not with VLPVpx. In the absence of SAMHD1 expression, either by targeting its degradation with VLPVpx (D; MT-4) or due to lack of expression (E; Jurkat), AZT antiviral activity is decreased. Means ± standard deviations (SD) from at least 2 independent experiments performed in duplicate are shown. MDM, monocyte-derived macrophages. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0005.