FIG 1.
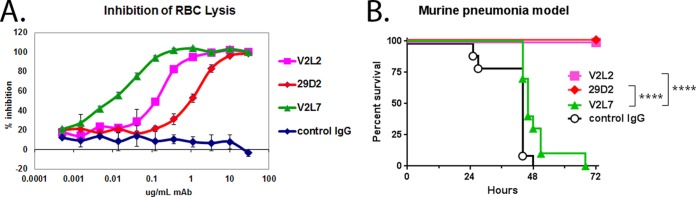
Evaluation of purified IgG from anti-PcrV hybridoma clones vitro and in vivo. (A) To quantitatively compare the ability of anti-PcrV hybridoma clones to inhibit P. aeruginosa T3SS in vitro, washed rabbit red blood cells (RBC) were incubated with log-phase P. aeruginosa strain 6077 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of purified IgG. The percent inhibition was determined by comparing the OD values from the test wells to the OD value in the control wells, which received no IgG. Error bars represent the standard deviations for four replicate samples. (B) The protective activities of anti-PcrV hybridoma clones were evaluated in a murine acute pneumonia model. BALB/c mice (n = 10) were treated with control IgG or the indicated clone at 25 mg/kg at 24 h before intranasal infection with strain 6077 (1e6 CFU). The animals were monitored for survival up to 72 h after infection. The results are represented as Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Differences in survival were calculated by the log rank test for V2L2 versus V2L7 (P < 0.0001) and for 29D2 versus V2L7 (P < 0.0001). Significance calculations for figures were performed with GraphPad Prism software, which assigns a number of asterisks to symbolically represent minimal significance (*) to high significance (****).
