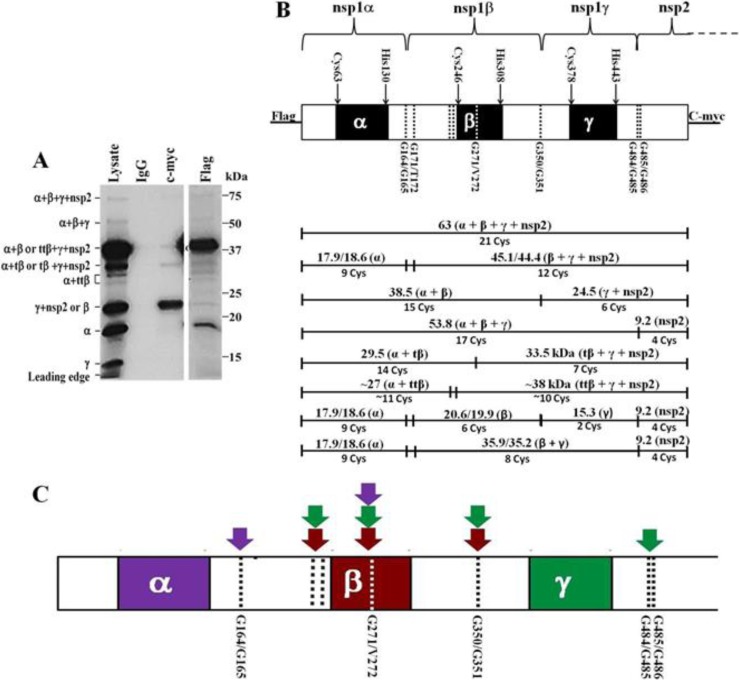
FIG 2.
SHFV nsp1 polyprotein cleavage map. The N-terminal 1,725 nt of SHFV ORF1a were cloned into the pTNT vector. The polyprotein expressed had an N-terminal Flag tag and a C-terminal c-Myc tag. (A) Products of the wild-type SHFV nsp1 polyprotein autoprocessing. The wild-type cDNA was in vitro transcribed and translated in a coupled TNT reaction (Promega) as described in Materials and Methods. Protein products labeled by incorporation of [35S]Cys were immunoprecipitated with murine IgG, anti-c-Myc, or anti-Flag antibody prior to separation by 13% SDS-PAGE. The positions of protein standards are indicated on the right, and the identities of the SHFV peptides generated are indicated on the left. (B) Diagram showing the relative locations of the predicted PLP1 domains and cleavage sites in the SHFV nsp1 polyprotein and the predicted cleavage products. (Top panel) Black boxes indicate the predicted PLP1 domains, and dotted lines indicate the cleavage sites. (Bottom panel) The sizes and identities of the predicted cleavage products are indicated above the lines, and the number of Cys residues in each peptide is indicated below the lines. (C) The sites shown by the data to be cleaved by each SHFV PLP1 in in vitro autoprocessing reactions are indicated by color-coordinated arrows.