Abstract
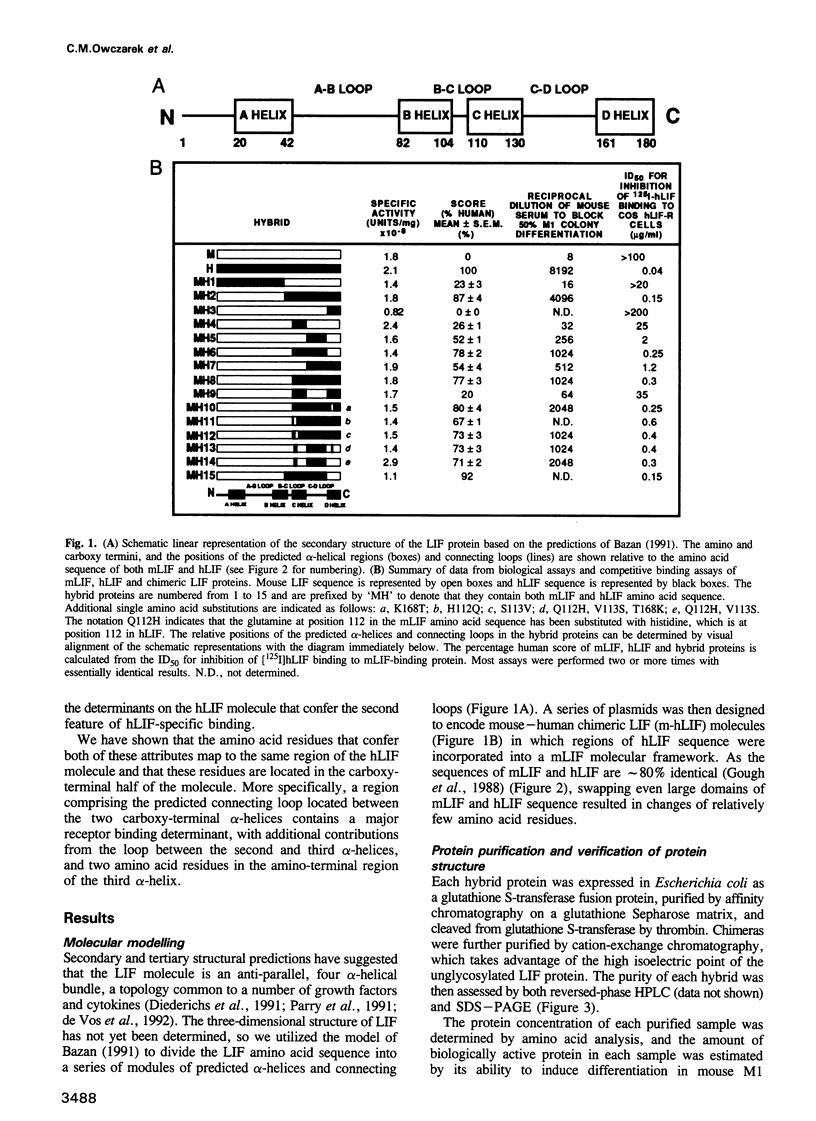
Human leukaemia inhibitory factor (hLIF) binds to both human and mouse LIF receptors (LIF-R), while mouse LIF (mLIF) binds only to mouse LIF-R. Moreover, hLIF binds with higher affinity to the mLIF-R than does mLIF. In order to define the regions of the hLIF molecule responsible for species-specific interaction with the hLIF-R and for the unusual high-affinity binding to the mLIF-R, a series of 15 mouse/human LIF hybrids has been generated. Perhaps surprisingly, both of these properties mapped to the same region of the hLIF molecule. The predominant contribution was from residues in the loop linking the third and fourth helices, with lesser contributions from residues in the third helix and the loop connecting the second and third helices in the predicted three-dimensional structure. Since all chimeras retained full biological activity and receptor-binding activity on mouse cells, and there was little variation in the specific biological activity of the purified proteins, it can be concluded that the overall secondary and tertiary structures of each chimera were intact. This observation also implied that the primary binding sites on mLIF and hLIF for the mLIF-R were unaltered by inter-species domain swapping. Consequently, the site on the hLIF molecule that confers species-specific binding to the hLIF-R and higher affinity binding to the mLIF-R, must constitute an additional interaction site to that used by both mLIF and hLIF to bind to the mLIF-R. These studies define a maximum of 15 amino acid differences between hLIF and mLIF that are responsible for the different properties of these proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Shieh H. S., Smith W. W., Dayringer H. E., Violand B. N., Bentle L. A. Three-dimensional structure of a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6434–6437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Haemopoietic receptors and helical cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Oct;11(10):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90139-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Shared architecture of hormone binding domains in type I and II interferon receptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):753–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90182-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Unraveling the structure of IL-2. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):410–413. doi: 10.1126/science.1631562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandhuber B. J., Boone T., Kenney W. C., McKay D. B. Crystals and a low resolution structure of interleukin-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12306–12308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher L. A., Tomkins J. K. A comparison of silver staining methods for detecting proteins in ultrathin polyacrylamide gels on support film after isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;148(2):384–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Yancopoulos G. D. The molecular biology of the CNTF receptor. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederichs K., Boone T., Karplus P. A. Novel fold and putative receptor binding site of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1779–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1837174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo M. T., Cabibbo A., Iacopetti P., Fattori E., Ciliberto G. Analysis of human/mouse interleukin-6 hybrid proteins: both amino and carboxy termini of human interleukin-6 are required for in vitro receptor binding. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2609–2615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga R., Ishizaka-Ikeda E., Seto Y., Nagata S. Expression cloning of a receptor for murine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90814-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M binds the high-affinity leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. New Biol. 1992 Jan;4(1):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Thut C. J., VandeBos T., Gimpel S. D., Delaney P. B., King J., Price V., Cosman D., Beckmann M. P. Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor is structurally related to the IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Gearing D. P., King J. A., Willson T. A., Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Molecular cloning and expression of the human homologue of the murine gene encoding myeloid leukemia-inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A. Kinetic analyses of the binding of leukemia inhibitory factor to receptor on cells and membranes and in detergent solution. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10238–10247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Specific binding of murine leukemia inhibitory factor to normal and leukemic monocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5971–5975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallestad J. C., Shoyab M., Linsley P. S. Disulfide bond assignment and identification of regions required for functional activity of oncostatin M. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8940–8945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Shanafelt A. B. GM-CSF receptor: interactions and activation. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse N., Tony H. P., Sebald W. Conversion of human interleukin-4 into a high affinity antagonist by a single amino acid replacement. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3237–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuga T., Komatsu Y., Yamasaki M., Sekine S., Miyaji H., Nishi T., Sato M., Yokoo Y., Asano M., Okabe M. Mutagenesis of human granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton M. J., Cross B. A., Metcalf D., Ward L. D., Simpson R. J., Nicola N. A. A major binding protein for leukemia inhibitory factor in normal mouse serum: identification as a soluble form of the cellular receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8616–8620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leebeek F. W., Fowlkes D. M. Construction and functional analysis of hybrid interleukin-6 variants. Characterization of the role of the C-terminus for species specificity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 20;306(2-3):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81013-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leebeek F. W., Kariya K., Schwabe M., Fowlkes D. M. Identification of a receptor binding site in the carboxyl terminus of human interleukin-6. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14832–14838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokker N. A., Movva N. R., Strittmatter U., Fagg B., Zenke G. Structure-activity relationship study of human interleukin-3. Identification of residues required for biological activity by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10624–10631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokker N. A., Zenke G., Strittmatter U., Fagg B., Movva N. R. Structure-activity relationship study of human interleukin-3: role of the C-terminal region for biological activity. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck D. N., Gout P. W., Beer C. T., Smith M. Bioactive recombinant methionyl bovine prolactin: structure-function studies using site-specific mutagenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 May;3(5):822–831. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-5-822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie A. N., Barry S. C., Strath M., Sanderson C. J. Structure-function analysis of interleukin-5 utilizing mouse/human chimeric molecules. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Hilton D. J., Nicola N. A. Clonal analysis of the actions of the murine leukemia inhibitory factor on leukemic and normal murine hemopoietic cells. Leukemia. 1988 Apr;2(4):216–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Int J Cell Cloning. 1991 Mar;9(2):95–108. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530090201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Hara T., Kitamura T. Common subunits of cytokine receptors and the functional redundancy of cytokines. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):378–382. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90004-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison B. W., Leder P. A receptor binding domain of mouse interleukin-4 defined by a solid-phase binding assay and in vitro mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11957–11963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
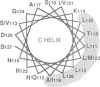
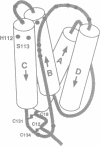
- Parry D. A., Minasian E., Leach S. J. Cytokine conformations: predictive studies. J Mol Recognit. 1991 Mar-Jun;4(2-3):63–75. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Garrett D. S., March C. J., Frieden E. A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Three-dimensional solution structure of human interleukin-4 by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1673–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose T. M., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8641–8645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda T., Shimazu T., Matsuda S., Kawano G., Shimizu H., Nakamura K. T., Mitsui Y. Three-dimensional crystal structure of recombinant murine interferon-beta. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3193–3201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., Nice E. C., Grego B., Yoshizaki F., Sugimura Y., Freeman H. C., Murata M. Complete amino acid sequence of plastocyanin from a green alga, Enteromorpha prolifera. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 16;157(3):497–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasueda H., Miyasaka Y., Shimamura T., Matsui H. Effect of semi-random mutagenesis at the C-terminal 4 amino acids of human interleukin-6 on its biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 31;187(1):18–25. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]