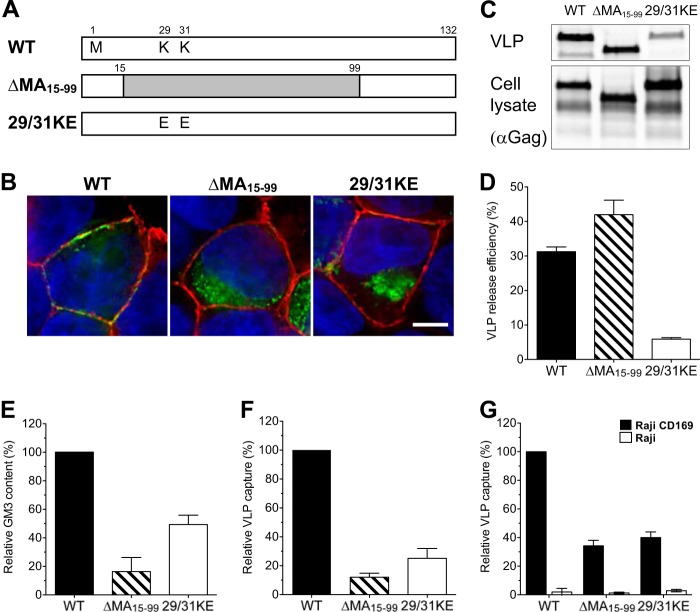
FIG 1.
MA mutant Gag-eGFP VLPs bud from intracellular membranes, and capture of HIV-1 Gag-eGFP VLPs by mature DCs is MA dependent. (A) Construction of HIV-1 matrix mutants. (B) Localization of eGFP fusion proteins in transfected HEK293T cells stained with CTxB-Alexa 594 for GM1 (red) and with DAPI for the nucleus (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of VLPs produced from transfected HEK293T cells was performed by probing with an anti-p24Gag monoclonal antibody. (D) Efficiency of VLP release from HEK293T cells. The amount of p24Gag in transfected HEK293T cell lysates and supernatants was quantified, and VLP release efficiencies were calculated [release efficiency = amount of p24Gag in the supernatant/(amount of p24Gag in the cell lysates + amount of p24Gag in the supernatant)]. The data shown are the means of triplicate experiments ± SDs. WT, wild-type Gag-eGFP; Δ15-99, ΔMA15-99-eGFP; 29/31KE, 29/31KE-eGFP. (E) The amount of VLP-associated GM3 was quantified by immunofluorescence staining. The value was normalized to that of wild-type Gag-eGFP. The experiment was performed on at least two independent VLP preparations, and the data are reported as the means ± SEMs of a representative experiment. (F) Mature DCs were challenged with VLPs and analyzed for GFP-positive cells by FACS. The percentage of GFP-positive DCs was normalized to that of wild-type Gag-eGFP VLPs. The results represent the means ± SEMs from four independent experiments performed on DCs from four different donors. (G) Raji-CD169 cells or Raji cells were challenged with VLPs, washed, and analyzed for GFP-positive cells. The value was normalized to that of wild-type Gag-eGFP capture by Raji-CD169 cells. The experiment was performed in triplicate at least two independent times, and the data from a representative experiment are shown as the means ± SDs.