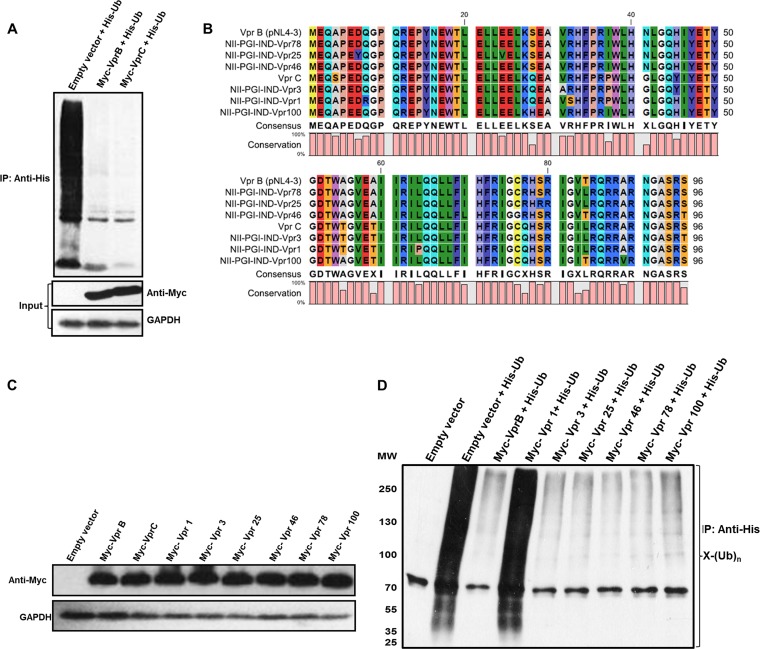
FIG 4.
Comparison of HIV-1 subtypes B and C and natural variants. (A) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with Myc-VprB/VprC and His-Ub. After 36 h, MG132 treatment was given for 8 h, and ubiquitinated proteins were enriched by using Ni-NTA beads (as described in Materials and Methods). Immunoblotting was done by using an anti-His antibody to probe whole-cell ubiquitination. Levels of Myc-VprB and subtype C are shown as the input. (B) Protein sequence alignment of HIV-1 VprB, VprC, and 6 samples. (C) The expression levels of 6 variant samples (Vpr-1, -3, -25, -46, -78, and -100), Myc-VprB, and Myc-VprC were checked in HEK 293T cells and normalized. (D) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with Myc-VprB, 6 variant samples (Vpr-1, -3, -25, -46, -78, and -100), and His-Ub. After 36 h, MG132 treatment was given for 8 h, and ubiquitinated proteins were enriched by using Ni-NTA beads (as described in Materials and Methods). Immunoblotting was done by using an anti-His antibody to probe whole-cell ubiquitination. GAPDH was used as a loading control.