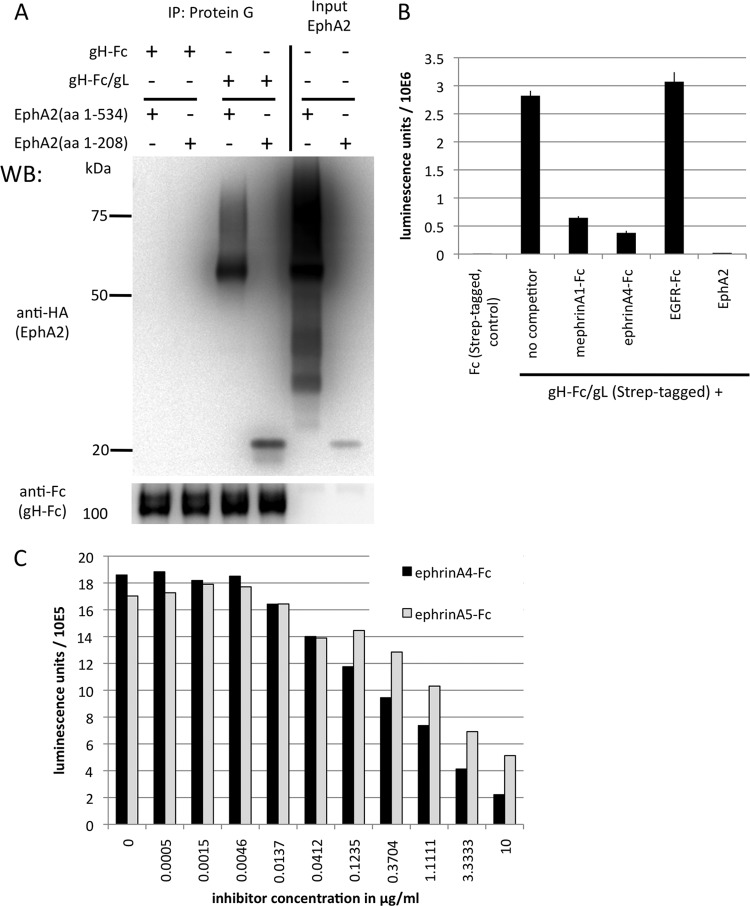
FIG 2.
KSHV gH/gL binds to the ligand binding domain of EphA2, and the interaction can be competed with ephrins. (A) KSHV gH/gL interacts with the ligand binding domain of EphA2. 293T cells were transfected with expression constructs for the complete soluble EphA2 ectodomain (amino acids [aa] 1 to 534) or the ligand binding domain (aa 1 to 208), both fused C terminally to a hemagglutinin (HA) tag. Equal amounts of cell culture supernatants from cells expressing the complete EphA2 ectodomain or the ligand binding domain were mixed with equal amounts of supernatants from cells transfected with expression plasmids for either soluble gH-Fc alone or gH-Fc and gL, which leads to a soluble gH-Fc/gL complex. After immunoprecipitation (IP) of gH-Fc or gH-Fc/gL with protein G Sepharose beads, samples were analyzed by Western blotting. The input lanes were loaded with the supernatants from cells transfected with constructs encoding the EphA2 ectodomain (aa 1 to 534) or the ligand binding domain (aa 1 to 208). (B) KSHV gH/gL binding to EphA2 can be competed with soluble ephrins. An ELISA plate was coated with recombinant soluble EphA2 ectodomain. The plate was then incubated with gH-Fc/gL at 1 μg/ml in the presence of mephrin A1-Fc, ephrin A4-Fc, EGFR-Fc as a control, and EphA2 (the same protein used for coating) as an assay control, all at 5 μg/ml. Bound gH-Fc/gL was detected with Streptactin-HRP, specifically recognizing a C-terminal tandem Strep tag on gH-Fc that is not present on the two ephrin-Fc proteins. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of gH-Fc/gL binding by ephrin A4-Fc and ephrin A5-Fc. Binding of gH-Fc/gL to immobilized EphA2 in the presence of various concentrations of ephrin A4-Fc or ephrin A5-Fc was measured as for panel B. Each data point represents a duplicate measurement.