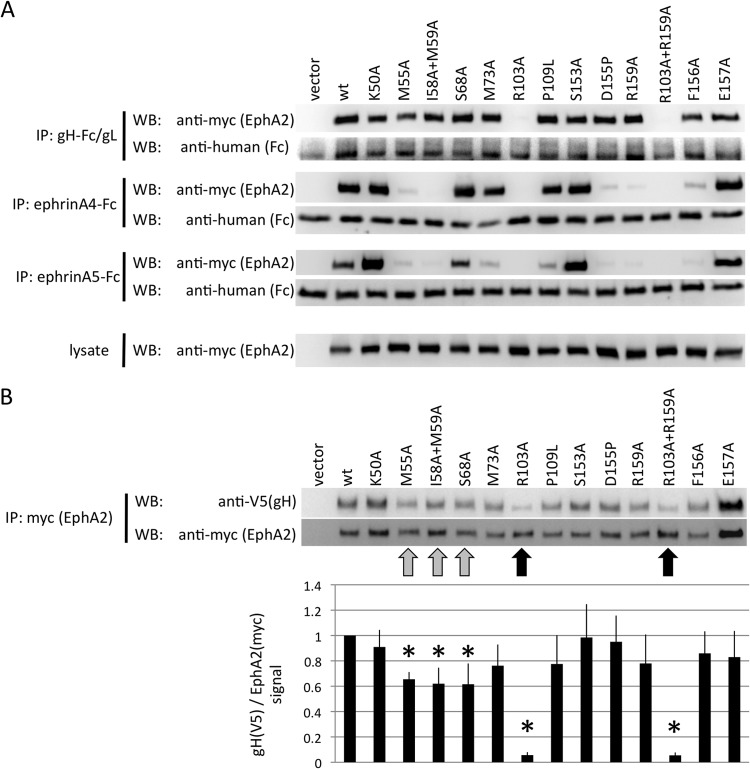
FIG 5.
KSHV gH/gL and ephrins interact with an overlapping set of residues on the surface of EphA2. (A) Immunoprecipitation of EphA2 point mutants with KSHV gH-Fc/gL, ephrin A4-Fc, or ephrin A5-Fc. The indicated EphA2 (myc epitope-tagged full-length EphA2) point mutants were recombinantly expressed in 293T cells. Cellular lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with protein G beads that were preadsorbed with either supernatant from gH-Fc/gL-expressing cells (top), 500 ng of recombinant ephrin A4-Fc (2nd from top), or ephrin A5-Fc (3rd from top) protein. Samples were analyzed by Western blotting as indicated. The expression level of each mutant in the lysate is shown in the bottom blots. (B) 293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids for the indicated EphA2 mutants (myc epitope tagged), and lysates were prepared 2 days after transfection. The myc epitope-tagged EphA2 mutants were immobilized to protein G Sepharose through immunoprecipitation with anti-myc monoclonal antibody. After aspiration of the lysate, equal amounts of cell lysate prepared from 293T cells that had been transfected with expression plasmids for KSHV gH (V5 epitope tagged) and gL were added to the immobilized EphA2 mutants. After 4 h of incubation, the samples were washed and analyzed by Western blotting. One representative Western blot is shown. The ratio of the signals for gH (V5) to EphA2 (myc) was calculated (bottom) from five independent experiments. The signal ratio for the wt was set to 1 for each independent experiment. Reductions in binding compared to the wt that reached significance (P < 0.05; Student's one-tailed t test) are marked with asterisks. The error bars represent the standard errors of the mean.