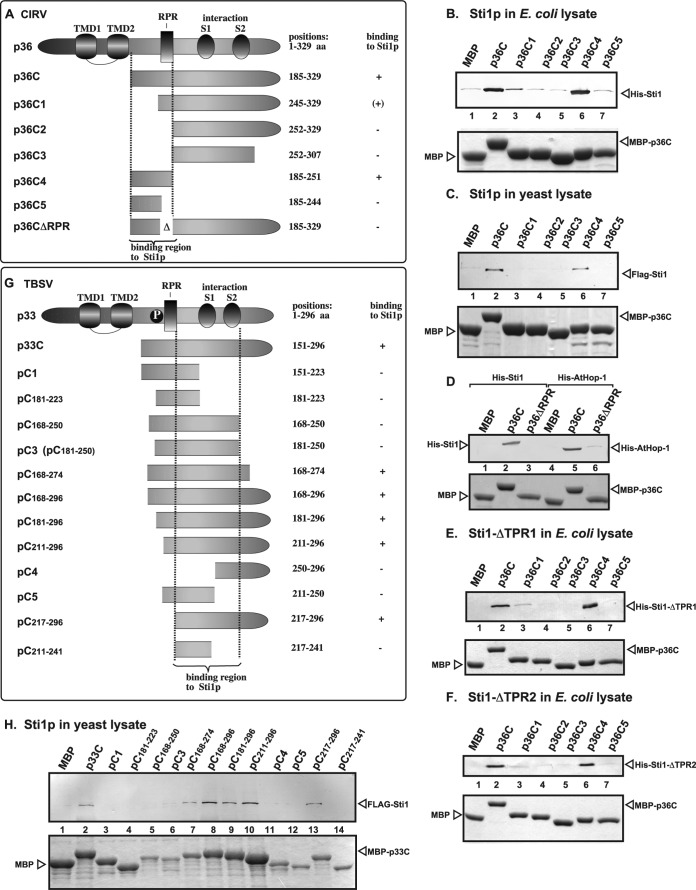
FIG 4.
Defining the sequence within the tombusvirus replication proteins needed for binding to Sti1p in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the CIRV p36 and its truncated derivatives used in the binding assay. The various domains include the transmembrane domain (TMD), the arginine- and proline-rich (RPR) RNA-binding domain, the phosphorylated serine and threonine (P) domain, and the S1 and S2 subdomains involved in p36-p36/p95 interaction. (B to F) Affinity binding (pulldown) assay to detect interaction between Flag- or His6-Sti1p, ΔTPR1, ΔTPR2, AtHop1, and the MBP-tagged CIRV p36 protein derivatives. The MBP-tagged viral proteins produced in E. coli were immobilized on amylose affinity columns. The recombinant Sti1p and derivatives expressed in E. coli (panels B, D, E, and F) or in yeast (panel C) were then passed through the amylose affinity columns with immobilized MBP-tagged p36 protein (its truncated versions). The affinity-bound proteins were eluted with maltose from the columns (shown in the bottom image). Top images in each panel, eluted proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Flag or anti-His antibodies to detect the amount of Flag- or His6-Sti1p specifically bound to MBP-tagged viral proteins. Bottom images, SDS-PAGE analysis of the viral protein and its truncated derivatives after elution from the amylose affinity columns. Note that the MBP has a C-terminal extra tail sequence (not present in the fusion protein constructs) due to the sequence in the original cloning vector. (G) Schematic representation of the TBSV p33 and its truncated derivatives used in the binding assay. (H) Affinity binding (pulldown) assay to detect interaction between FLAG-Sti1p and the MBP-tagged viral p33 protein (the soluble C-terminal portion). The MBP-tagged viral protein or MBP control produced in E. coli was immobilized on amylose affinity columns. See further details in legend to panel B. The eluted proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody to detect the amount of FLAG-Sti1p specifically bound to MBP-tagged viral protein.