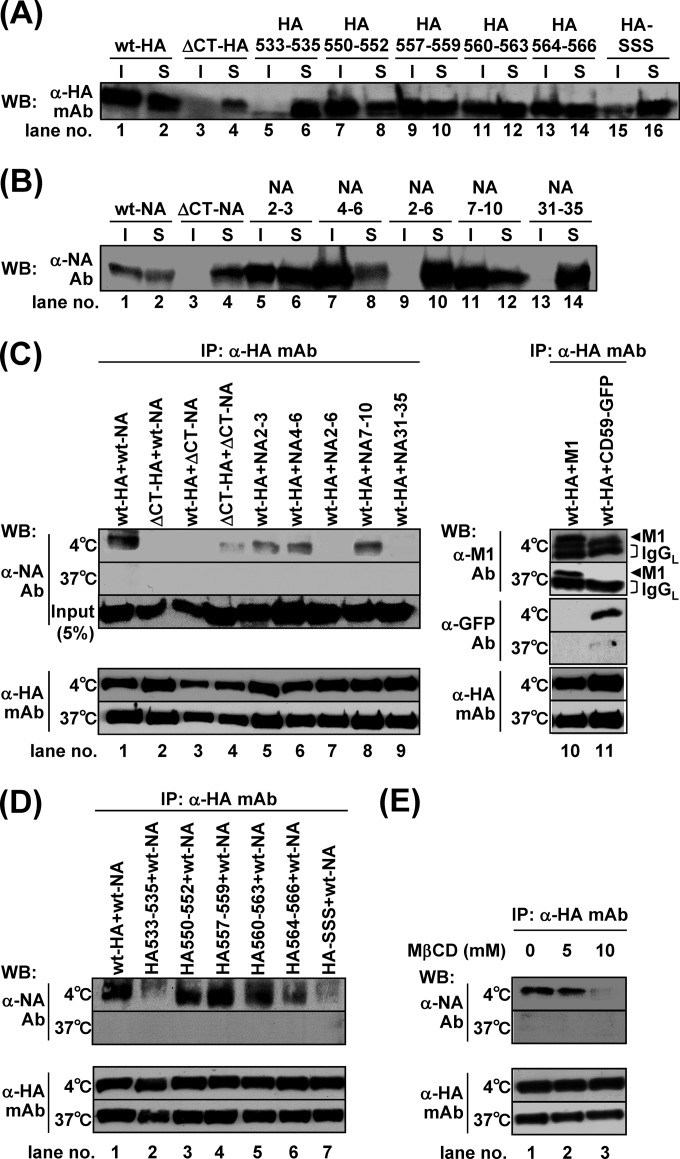
FIG 6.
TX-100 solubility of HA and NA and interaction of HA and NA through lipid rafts. For the TX-100 solubilization test, 293T cells were singly transfected with mutant HA (A) or NA (B) expression plasmids (indicated). The cells were lysed with TNE buffer containing 1% TX-100 at 4°C for 30 min. Insoluble (I) and soluble (S) fractions were separated by centrifugation. For the interaction of HA and NA, cells were cotransfected with wt-HA and mutant NA expression plasmids (indicated) (C) or with mutant HA and wt-NA expression plasmids (indicated) (D). M1 was used as a positive control for direct interaction with HA, and GFP-CD59 was used as a marker for lipid rafts. The cells were lysed with TNE buffer containing 1% TX-100 at 4°C or 37°C for 30 min and were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation with anti-HA mAb12-1G6. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using sheep anti-NA, anti-M1, and anti-GFP Abs and anti-HA mAb12-1G6. (E) For the cholesterol depletion experiment, 293T cells were pretreated with lovastatin for 12 h, cotransfected with wt-HA and wt-NA expression plasmids, and incubated at 37°C in the presence of lovastatin. At 24 hpt, the cells were further treated with lovastatin plus 5 mM or 10 mM MβCD for 1 h and were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation experiments. WB, Western blotting; mAb, mAb12-1G6; IP, immunoprecipitation.