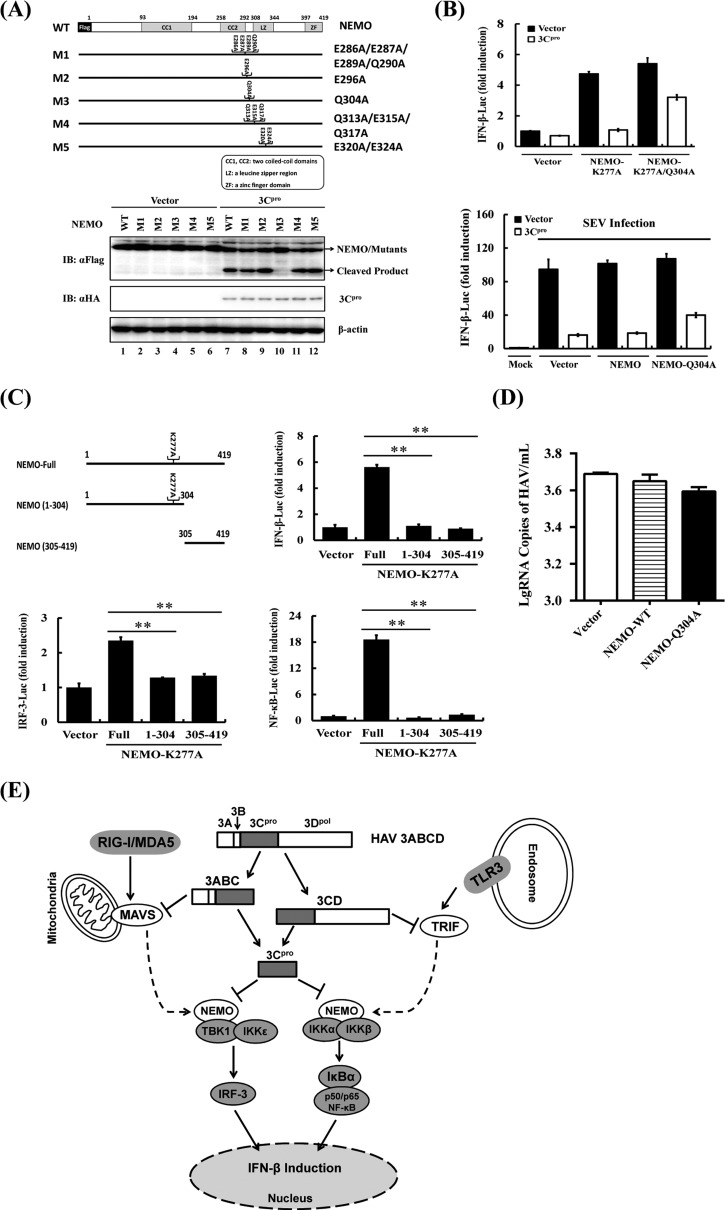
FIG 4.
HAV 3Cpro-mediated NEMO cleavage is involved in the inhibition of IFN-β induction. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type NEMO and its derivatives (top). HEK293T cells cultured in 60-mm-diameter dishes were transfected with Flag-tagged wild-type NEMO or NEMO mutants as indicated, along with HA-3Cpro or empty vector. Cell lysates were prepared 30 h posttransfection and analyzed by Western blotting. (B) HEK293T cells cultured in 24-well plates were cotransfected with IFN-β-Luc, pRL-TK plasmid, and plasmid encoding 3Cpro (0.3 μg) together with the empty vector, NEMO-K277A, or the NEMO-K277A/Q304A expression vector (0.7 μg). Luciferase assays were performed 36 h after transfection (top). HEK293T cells cultured in 24-well plates were cotransfected with IFN-β-Luc, pRL-TK plasmid, and plasmid encoding 3Cpro (0.3 μg) together with the empty vector, NEMO, or the NEMO-Q304A expression vector (0.7 μg). Twenty-four hours after the initial transfection, the cells were further infected or mock infected with SEV. Luciferase assays were performed at 16 h after infection (down). (C) HEK293T cells cultured in 24-well plates were cotransfected with IFN-β-Luc, pRL-TK plasmid and either 1 μg of plasmid encoding Flag-fused NEMO-K277A (Full), putative 3Cpro-induced cleavage fragments of NEMO-K277A, or empty vector. Cell extracts were collected 36 h after transfection and analyzed for firefly and Renilla luciferase expression. **, P < 0.01 (considered highly significant). (D) HEK293T cells cultured in 24-well plates were transfected with the indicated NEMO-expressing plasmids and infected with HAV (L-A-1 attenuated vaccine strain; MOI of 1) 12 h posttransfection. The cells were lysed 36 h postinfection and analyzed by RT-qPCR according to the reference methods (21). (E) Type I interferon signaling pathways disrupted by HAV 3Cpro and its precursors. HAV 3Cpro and its processing intermediates disrupt IFN-β induction by 3ABC-mediated proteolysis of MAVS (9), 3CD-mediated proteolysis of TRIF (10), and 3Cpro-mediated proteolysis of NEMO in this study.