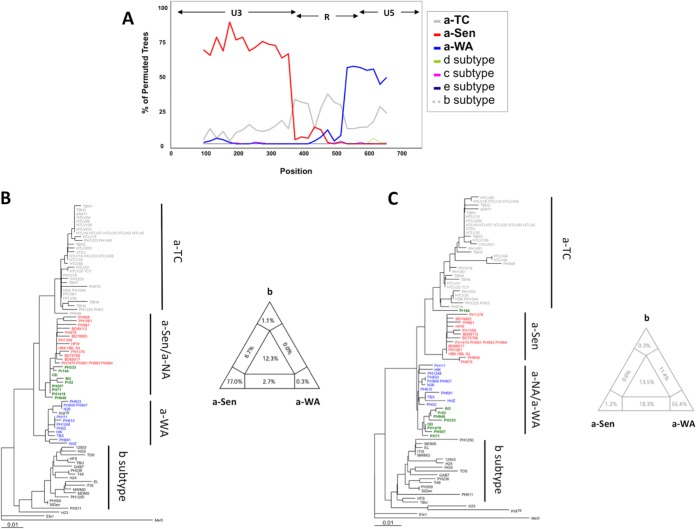
FIG 2.
a-NA strains derive from a recombination event. (A) The a-NA subgroup was compared by boot-scanning (Simplot program) to different clades (a-TC, a-WA, a-Sen, b, d, e, and c). The analysis used a 180-bp-long window and a 20 bp-long step. The x values reflect the genome position at the midpoint of the analyzed windows, and the y values reflect the bootstrap value calculated from the windows. (B and C) Phylogenetic trees corresponding to the first 375 nucleotides and the 399 last nucleotides, respectively, were derived from the neighbor-joining method (GTR; gamma = 0.5325). The groups of interest are colored as follows: red, green, and blue sequences belong to a-Sen, a-NA, and a-WA, respectively. In both trees, 4 informative sites determine the topology between the 3 clades of interest. The quartet mapping of each sequence fragment is presented.