FIG 3.
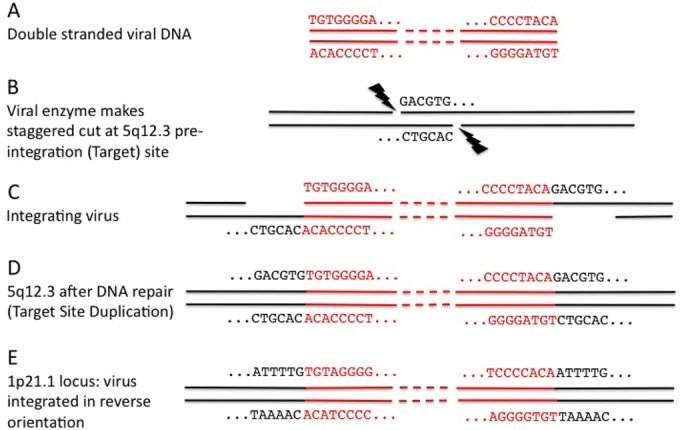
How chimeric reads result from ERV integration. (A to D) A guide to interpretation of outputs by use of locus 5q12.3 as an example. After reverse transcription, viral double-stranded DNA (red) is integrated into the chromosome. The viral integrase enzyme makes a staggered cut, typically of 6 nt, into which the viral DNA is inserted. DNA repair of the now single-stranded DNA on either side of the integration produces six identical nucleotides (the target site duplication) flanking the virus. (E) However, in some cases the virus has integrated in reverse orientation, and an example of where this has occurred is shown for locus 1p21.1. Note the changed viral sequence.
