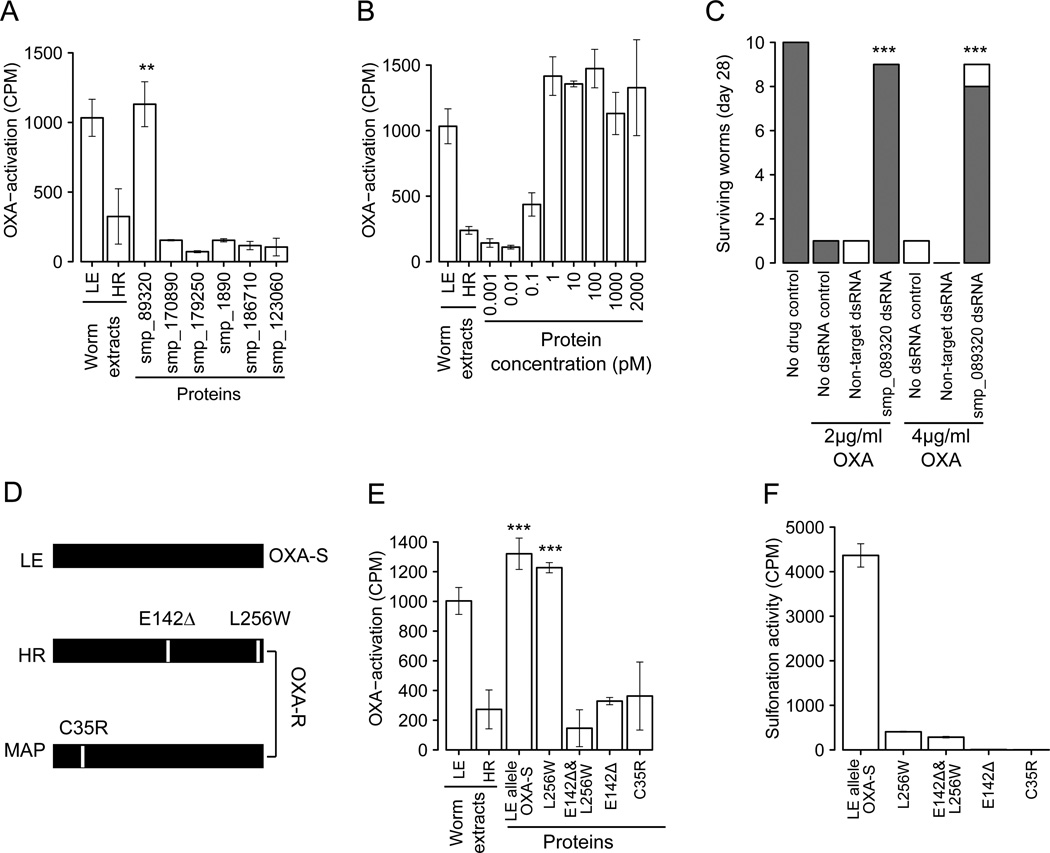
Fig. 2. Identification of gene and mutations underlying OXA-resistance.
(A) Complementation assays to identify proteins that restore OXA-binding in resistant worm homogenates. Extracts of LE (OXA-sensitive) and HR (OXA-resistant) worms were positive and negative controls. Error bars show 1 SD in triplicate assays. Significant increases in activation relative to the HR control are shown (** p<0.01). (B) Complementation using serial dilution of Smp-089320 protein. (C) RNAi knockdown of Smp-089320. Surviving worms were categorized as vigorous (shaded) or unwell (white) (Movie S1). Significant increase in survival relative to treated controls are marked (*** p<0.001) (D) Smp-089320 alleles from LE (OXA-sensitive) and two OXA-resistant parasites (HR, laboratory-selected; MAP, field-derived). (E) Identification of OXA-resistance mutations. Proteins bearing different mutations were used in OXA-complementation assays. Significant increases in activation relative to the HR control are shown (*** p<0.001). (F) Sulfonation activity of Smp-089320 alleles.