Figure 5. YAP-reprogrammed progenitors are clonogenic and produce hepatocyte progeny.
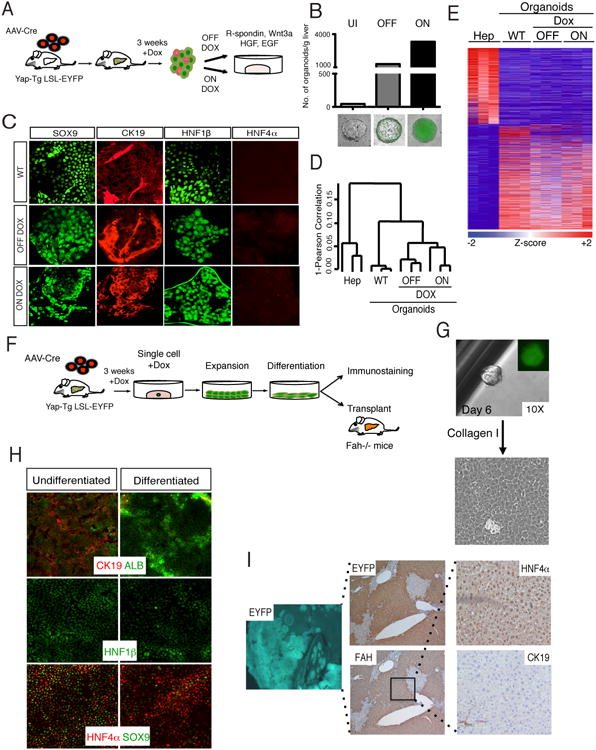
A. Schematic representation of liver organoid generation from YAP Tg mice and expansion procedure. B. Analysis of the number of organoids derived from livers from AAV-Cre infected Dox-uninduced (UI) and 3-week induced YAP Tg mice. YAP Tg results in dramatic increase of the liver organoid generation both in the presence (ON) and absence (OFF) of Dox in culture. Bottom shows representative immunofluorescent (IF) images of organoids in each category. Bars represent value of N=3. C. IF of wild-type (WT), ON Dox YAP Tg and OFF Dox YAP Tg organoids for biliary (SOX9, CK19, Hnf1β) and hepatocyte (HNF4α) markers. D. Hierarchical clustering analysis of primary hepatocytes, WT and hepatocyte-derived YAP Tg organoids demonstrates close clustering of all organoid groups. E. Differential expression analysis of hepatocytes compared to distinct organoid populations. Heat map demonstrates all differentially expressed genes with ≥ 2.5 fold change. F. Experimental design for the isolation, expansion and characterization of single-cell hepatocyte-derived organoids. G. Representative image of organoid derived from single sorted EYFP+ YAP Tg cell, followed by monolayer expansion. H. Differentiation of hepatocyte-derived organoid clone in the presence of γ-secretase inhibitor and in the absence of Dox. Day 15 differentiated cells demonstrate downregulation of biliary (CK19, SOX9, Hnf1β) and increase of hepatocyte markers (ALB, HNF4α). I. Representative liver images 5 months after transplantation of differentiated clonal YAP-Tg cells into Fah-/- mice. Engrafted cells are positive for EYFP (5×), FAH (5×) and HNF4α (hepatocyte marker), and negative for CK19 (biliary marker). See also Figure S5.
