Figure 6. YAP and TEAD regulates Notch2 transcription.
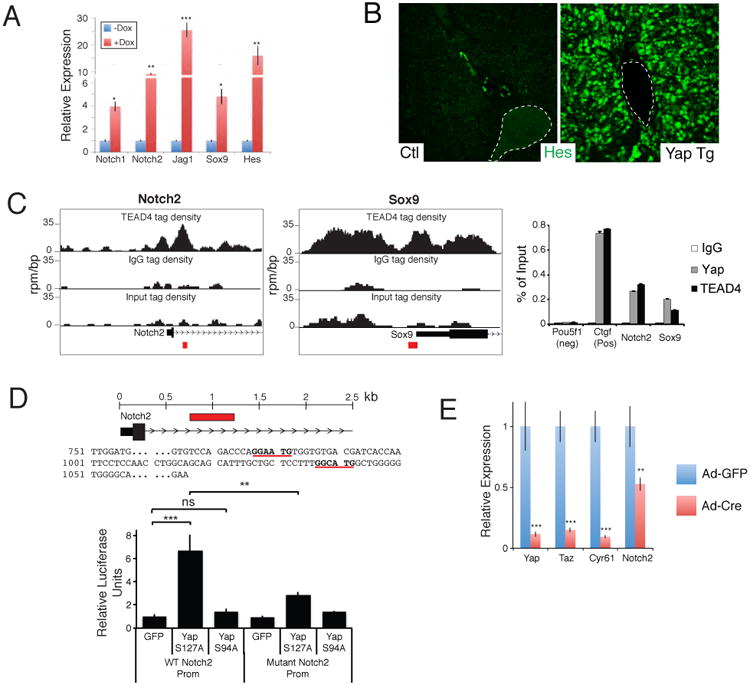
A. qRT-PCR analysis of NOTCH pathway genes from EYFP+ sorted uninduced and 1-week Dox YAP Tg liver cells post AAV-Cre infection. B. Immunofluorescent analysis for HES1 in an uninduced (Ctl) and a 2-week YAP Tg mouse. Dotted line outlines portal vein. C. ChIP-Seq binding profiles (reads per million per base pair) for TEAD4 at the Notch2 and Sox9 loci in trophoblast stem cells. Graph on the right shows ChIP-PCR assays for the indicated validation sites (red boxes) performed in liver cells isolated from YAP Tg mice 2 weeks post Dox . D. Localization and sequence of TEAD binding sites (bold and underlined) present in the NOTCH2 promoter. Red box indicates area of genomic sequence (WT Notch2 prom) that was cloned into a luciferase expression construct for functional analyses in CCLP1 cells (bottom). Mutant Notch2 promoter construct contains 3 mutated base pairs at each of the TEAD binding sites. n=3, mean +/- SEM. E. qPCR analysis of the indicated target genes in Yapfl/fl Tazfl/fl liver organoids given either Adenovirus-EGFP or Ad–Cre:EGFP. mRNA analysis of sorted infected cells was done 48 hours following infection. n=3, mean +/- SD. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. See also Figure S6.
