Figure 1. Novel Model of RP.
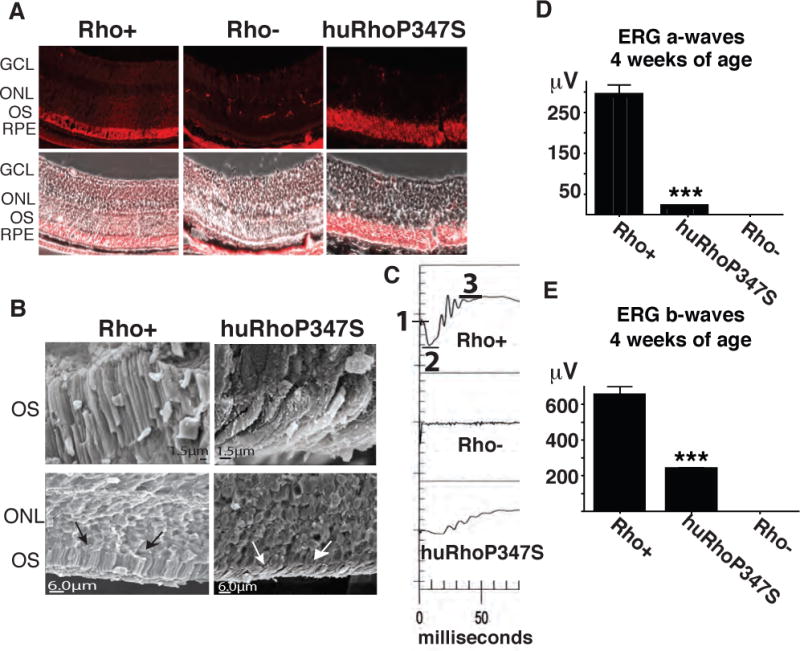
A) Rhodopsin localizes to photoreceptor outer segments (OS) in normal (Rho+) and to the ONL in huRhoP347S mice, but is not observed in rhodopsin null mice (Rho−) (magnification = 40X). Note: In Rho− retina, non-specific stain is observed in muscle tissue behind RPE. B) Scanning electron microscopy of normal (Rho+) and huRhoP347S mouse photoreceptor OS reveal shortened OS (white arrows) in huRhoP347S mice relative to those of Rho+ mice (black arrows). C) The huRhoP347S mice have decreased ERG a-waves and b-waves relative to mice with normal mouse rhodopsin (Rho+). Rhodopsin null (Rho−) mice do not exhibit a-waves or b-waves. Top panel illustrates ERG a-wave determination from baseline (1) to trough (2), and b-waves from trough (2) to crest (3). All recordings shown at 4 weeks of age. D) The huRhoP347S mice have a 15-fold reduction (***n=24, p<0.0001) in a-wave amplitudes relative to normal rhodopsin mice (Rho+) at 4 weeks of age. Rhodopsin null (Rho−) mice have no a-waves. E) The huRhoP347S mice have a 3-fold reduction (***n=24, p<0.0001) in b-wave amplitudes relative to normal rhodopsin mice (Rho+) at 4 weeks of age. Rhodopsin null (Rho−) mice have no b-waves. GCL, ganglion cell layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OS, outer segments; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.
