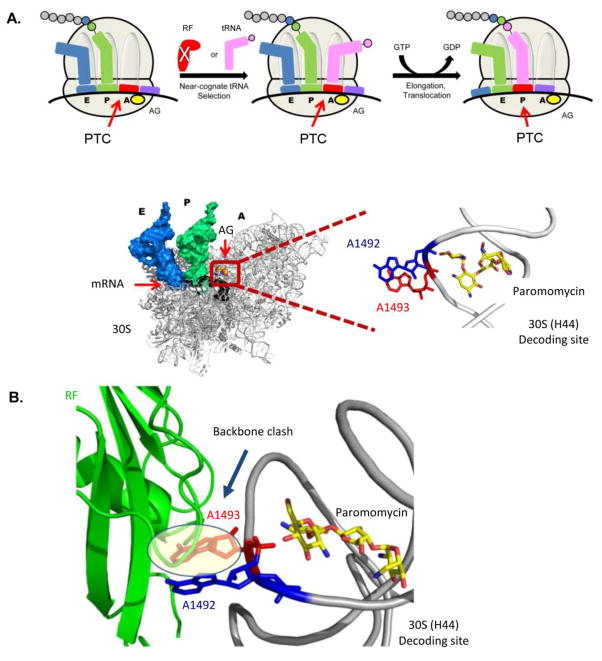
Figure 9.
The read-through mechanism. (A) Schematic representation of the read-through mechanism at the molecular level as indicated from recent X-ray structures (top panel). The structure at the bottom panel presents the A-site conformation upon AG (paromomycin) binding with the two conserved adenine residues (A1492-blue and A1493-red) bulging out from the helical core. PTC denotes Premature Termination Codon. (B) Superposition of the bacterial ribosome structure with the AG paromomycin (yellow sticks) bound to the A-site (PDB ID: 3IBL) and RF bound to the bacterial ribosome (PDB ID: 2X9R). The structure demonstrates the clashing of A1493 (red) with the Cα backbone of the RF (green), therefore suggests for a steric hindrance of RF to the A-site upon the induced conformation when AG is bound to the bacterial A-site.