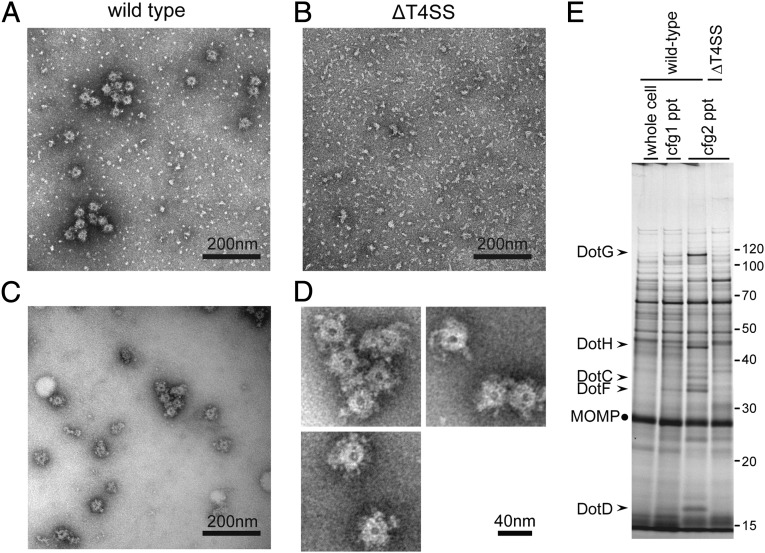
Fig. 2.
Isolation of ring structures with a diameter of ∼40 nm. Ring structures were enriched as described in Materials and Methods, mounted on grids, and stained with 2% (wt/vol) PTA pH 7.0. Transmission electron micrographs of fractions isolated from wild-type cells (A and C) and isogenic deletion mutant (ΔT4SS) cells lacking all dot/icm genes (B) are shown. (Scale bar, 200 nm.) (C) The fraction shown in A was further purified by a size exclusion column chromatography to remove small specks observed. (D) Isolated ring structures from wild-type cells. (Scale bar, 40 nm.) (E) Proteins visualized by silver staining of fractions during the isolation procedure. The procedure involves two consecutive ultracentrifugation processes (Materials and Methods). Starting lysate (whole cell) and pellet fractions after ultracentrifugations (cfg, 1/2 ppt) were analyzed. Five Dot/Icm proteins (arrowheads) were consistently enriched during the procedure. MOMP, the major outer membrane protein of L. pneumophila, is a major contaminant protein in this procedure and is used as an internal control for comparison.