Fig. 6.
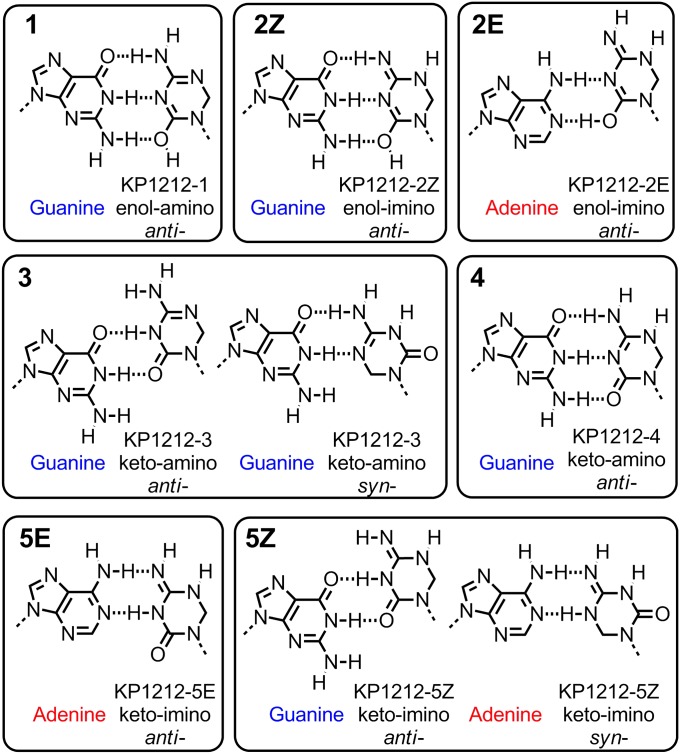
A mechanistic model explaining the mutagenesis of KP1212 by the distinct base-pairing preferences of its different tautomers. KP1212 tautomers are paired with purine bases (G or A), by maximizing the number of possible hydrogen bonds between the bases. Tautomers 1, 2Z, 4, and 5E have a canonical Watson–Crick face and therefore are proposed to pair exclusively with either G or A. The remaining tautomers are proposed to pair either in wobble position (2E, 3, and 5Z) or involving a syn-conformer of KP1212 (3 and 5Z).