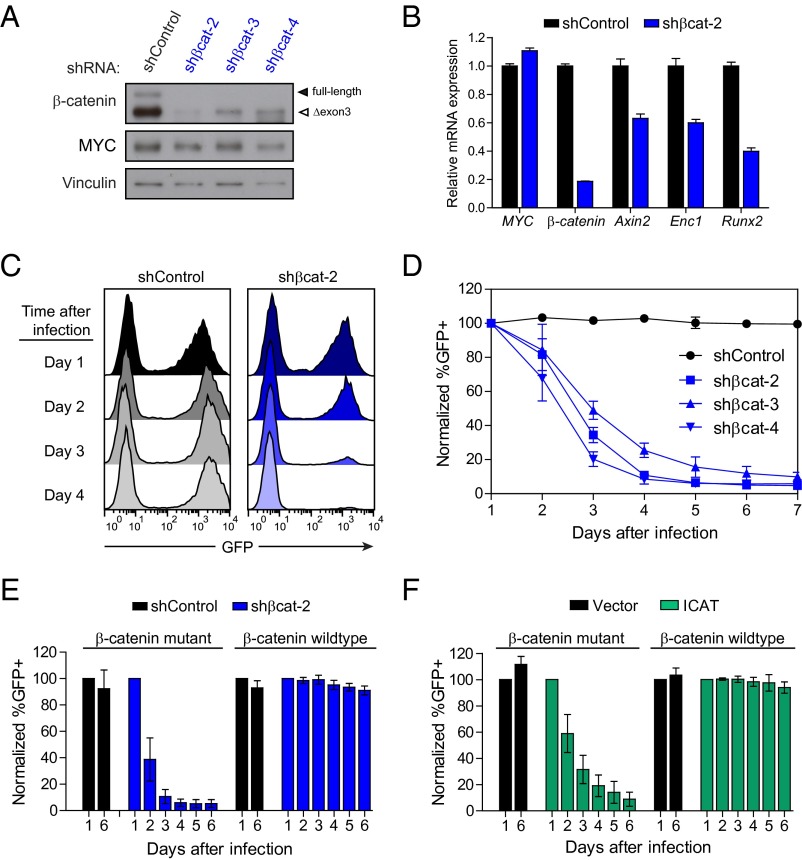
Fig. 2.
MYC-induced lymphomas exhibit addiction to mutant β-catenin. (A) Western blot analysis of MYC lymphoma cells retrovirally infected with either control shRNA (shControl) or three independent shRNAs targeting β-catenin (shßcat-2, shßcat-3, and shßcat-4). (B) Relative mRNA expression levels of transgenic MYC, β-catenin, and three β-catenin target genes (Axin2, Runx2, and Enc1) in MYC lymphoma cells infected with either control or β-catenin shRNA, as analyzed by qRT-PCR. (C) Representative histograms and (D) quantification of GFP fluorescence in MYC lymphoma cells after infection with either control or β-catenin shRNA coexpressing GFP. (E and F) Quantification of GFP fluorescence over time of MYC lymphoma cell lines mutant or WT for β-catenin and infected with retrovirus expressing either (E) β-catenin shRNA or (F) the β-catenin inhibitor ICAT. Values represent means ± SD of two cell lines with WT β-catenin and two cell lines with mutant β-catenin and three independent experiments per cell line. Data are normalized to the percentage of GFP+ cells at day 1 after infection.