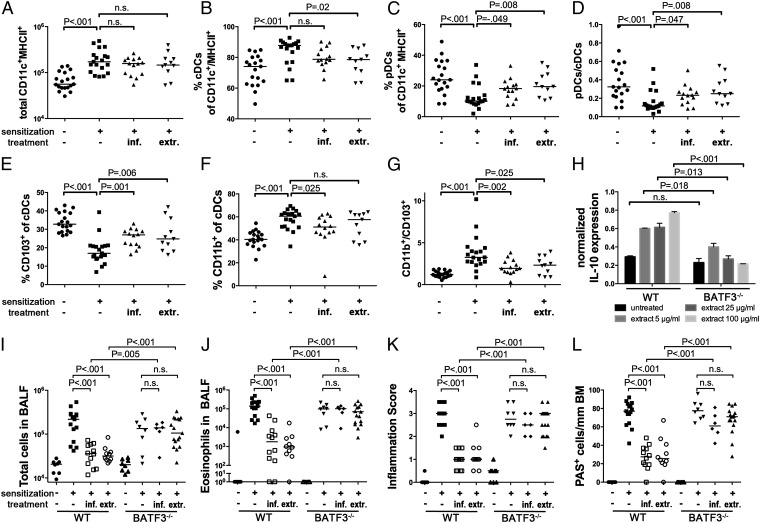
Fig. 3.
CD103+ conventional DCs accumulate in the lungs of H. pylori-infected and extract-treated mice and are required for protection. (A–G) Groups of mice treated as described in Figs. 1 and 2 were analyzed with respect to lung infiltration by pDCs and two lineages of cDCs. Data are pooled from three independent studies. (A) Total infiltration of CD11c+MHC+ cells. (B and C) Frequencies of B220− cDCs and B220+ pDCs among all CD11c+MHC+ cells. (D) Ratios of pDCs to cDCs as calculated per mouse. (E and F) Frequencies of CD103+ and CD11b+ cells among all cDCs. (G) Ratios of CD11b+ and CD103+ cDCs as calculated per mouse. (H) IL-10 transcript levels normalized to GAPDH, of immunomagnetically isolated CD11c+ DCs from mesenteric lymph nodes of WT and BATF3−/− mice, treated with the indicated increasing doses of H. pylori extract. (I–L) Wild-type and BATF3−/− mice were treated or infected as described in Figs. 1 and 2 and subjected to ovalbumin sensitization and challenge. (I and J) Total cells and eosinophils contained in 1 mL of BALF. (K and L) Tissue inflammation and goblet cell metaplasia.