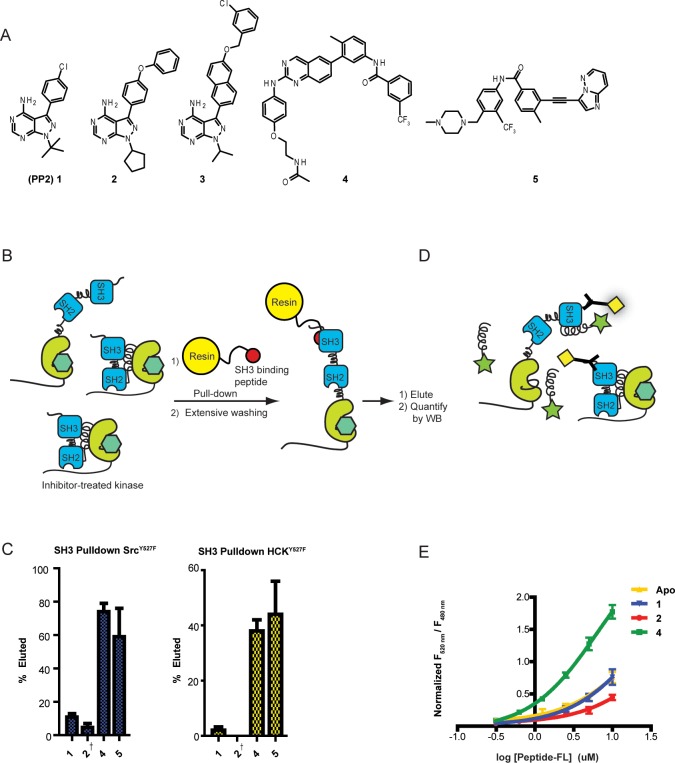
Figure 2.
Conformation-selective inhibitors divergently modulate the SH3 domain accessibility of Src and Hck. (A) Panel of inhibitors that were used in this study. 2 and 3 stabilize the αC helix-out inactive conformation. 4 and 5 stabilize the DFG-out inactive conformation. (B) SH3 domain accessibility pull-down assay. Src or Hck was incubated with an immobilized SH3 domain ligand in the presence of a saturating amount of an inhibitor (1, 2, 4, or 5). After incubation, beads were washed, and retained SFKs were eluted with SDS. Retained SFKs were quantified by immunoblotting. (C) Quantification of the pull-down experiments performed with SrcY527F and HckY527F in the presence of 1, 2, 4, or 5 (mean ± SEM, n = 3). † = Previously reported and shown for comparison.21 (D) FRET assay to measure intermolecular SH3 domain accessibility. Hck was incubated with conformation-selective inhibitors in the presence of variable concentrations of a fluorophore-labeled SH3 peptide ligand (Peptide-FL). SH3 domain accessibility was determined by measuring FRET between the donor His-Tb, which is bound to the N-terminal His6 tag of Hck, and Peptide-FL. (E) Binding of fluorophore-labeled SH3 peptide ligand (Peptide-FL) in the presence of conformation-selective inhibitors (mean ± SEM, n = 3).