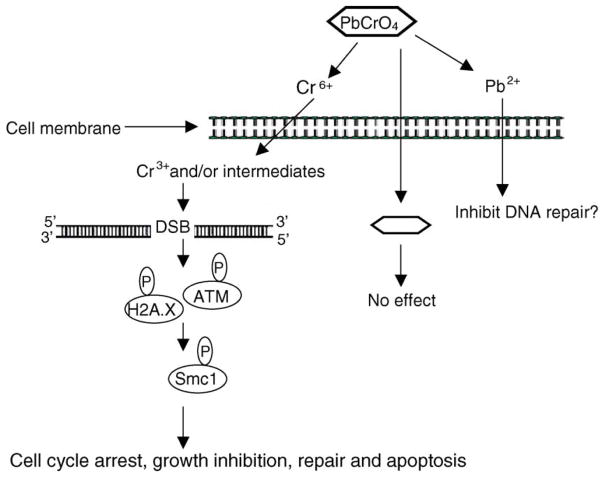
Fig. 8.
Proposed mechanism of particulate Cr(VI) genotoxicity. In response to DNA DSBs induced by Cr ions released from the extracellular dissolution of lead chromate, ATM kinases are activated. ATM, through the intermediacy of H2A.X, phosphorylates SMC1 on Ser 966 which leading to cell cycle arrest, growth inhibition, repair and apoptosis.