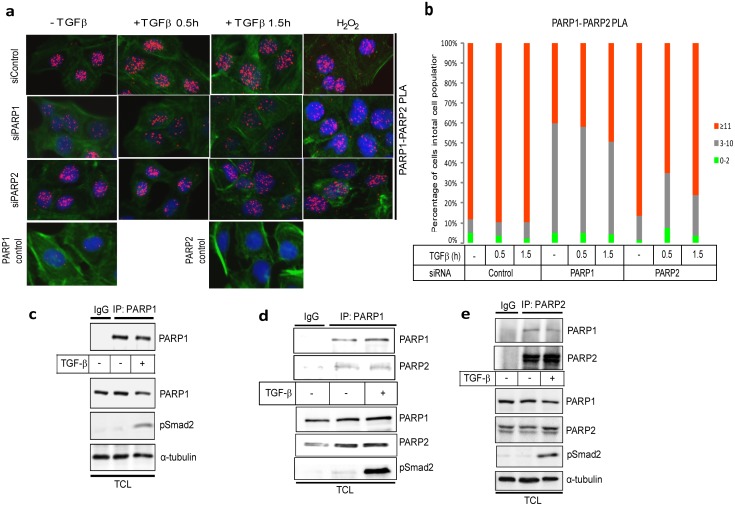
Figure 5. Analysis of endogenous PARP-1 and PARP-2 complexes in HaCaT cells.
(a) HaCaT cells were analyzed with PLA using antibodies against PARP-1 and PARP-2 after transfection with control or the indicated specific siRNAs and stimulation with vehicle (-TGFβ) or with 2 ng/ml TGFβ1 for the indicated time periods. Specific RCA signals were detected in the nuclei. Cells stimulated with 10 mM hydrogen peroxide for 10 min served as positive control. PLA with single antibodies against PARP-1 or PARP-2 are shown as controls. PLA images are shown as in Fig. 1a. (b) Quantification of the experiment shown in panel (a) following the histogram method of Fig. 1b. Panels a–b show a representative experiment from three or more repeats. (c) Immunoprecipitation of PARP-1 followed by immunoblotting for PARP-1 in HaCaT cells stimulated with vehicle (-TGFβ) or with 5 ng/ml TGFβ1 for 30 min. Negative control immunoprecipitation using non-specific IgG is shown. TCL shows the levels of endogenous proteins before immunoprecipitation. C-terminal phospho-Smad2 (p-Smad2) serves as control for the efficiency of stimulation of TGFβ signaling and α-tubulin as protein loading control. (d) Immunoprecipitation of PARP-1 followed by immunoblotting for PARP-1 and PARP-2 in HaCaT cells stimulated with vehicle (-TGFβ) or with 5 ng/ml TGFβ1 for 30 min. Negative control immunoprecipitation using non-specific IgG is shown. TCL shows the levels of endogenous proteins before immunoprecipitation. PARP-1 immunoblot also serves as protein loading control and C-terminal phospho-Smad2 (p-Smad2) serves as control for the efficiency of stimulation of TGFβ signaling. (e) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation of PARP-2 followed by immunoblotting for PARP-1 and PARP-2 in HaCaT cells stimulated with vehicle (-TGFβ) or with 5 ng/ml TGFβ1 for 30 min. Negative control immunoprecipitation using non-specific IgG is shown. TCL shows the levels of endogenous proteins before immunoprecipitation. C-terminal phospho-Smad2 (p-Smad2) serves as control for the efficiency of stimulation of TGFβ signaling and α-tubulin as protein loading control. Panels c–e show results from representative experiments that were repeated at least twice.