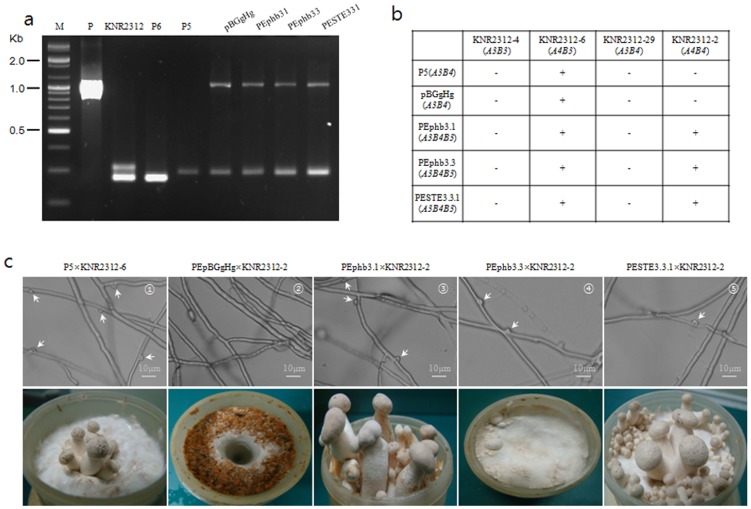
Figure 5. PCR band pattern for the confirmation of transformation, crossing table between the wild-type and transgenic monokaryons, and fruiting body (clamp connection) formation.
a: Specific DNA fragments obtained in test-crossed mycelia using hph (Table S1). P: positive marker (pBGgHg), KNR2312: a dikaryon consisting of P5 and P6, P6: a monokaryon, P5: a monokaryon, pBGgHg: a transformant with the empty vector (pBGgHg), P5phb31: a P5 transformant with PEphb3.1, P5phb33: a P5 transformant with PEphb3.3, P5STE331: a P5 transformant with PESTE3.3.1, b: Wild-type tester strains (KNR2312-4: A3B3, KNR2312-6: A3B4, KNR2312-29: A4B3, and KNR2312-2: A4B4) were used for crosses with the transgenic monokaryons with the empty vector or with the pheromone or receptor genes, c: Clamp connections and fruiting bodies were observed in the positive control (wild type) (1) and dikaryons mated with transgenic monokaryons and the tester strain (3 and 5), but none were observed in the incompatible combination (2). In the case of 4, only primordia were shown. Labels above the panels indicate the cross combinations.