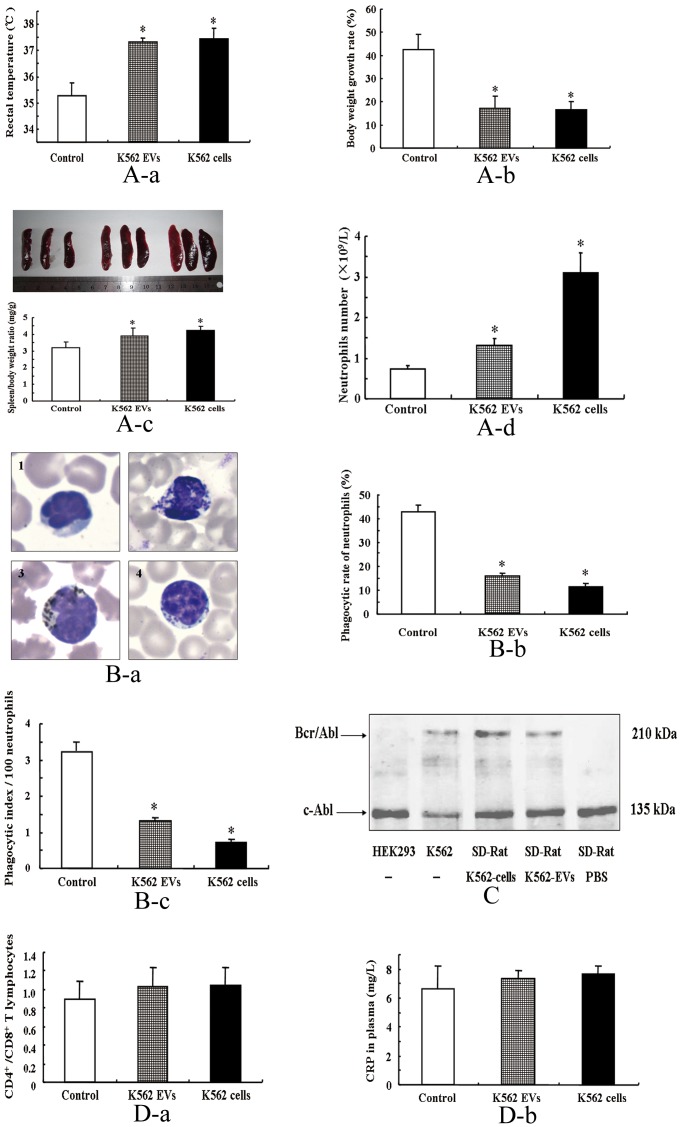
Figure 1. Effect of K562 EVs on several pathophysiological parameters in SD rats.
(A): Pathophysiological parameters in SD rats bearing K562 EVs. SD rats were injected, via tail-vein, with K562 cells (2×106), K562-derived-EVs (2×106) or vehicle (PBS). Rectal temperature (a), body weight gain (b), spleen to body weight ratio (c), and neutrophils count (d) were obtained at 12week-old of age (* P<0.05 vs. control n = 3). (B): Phagocytic activity of neutrophils in SD rats bearing K562 EVs. (a): Representative images of India ink-exposed neutrophils. 1. neutrophils from SD control rat without incubation with ink; 2. neutrophils from SD control rat; 3. neutrophils from K562 EVs-bearing SD rat; 4. neutrophils from K562 cell-bearing SD rat. (b) and (c): SD rats injected via tail-vein with K562 cells (2×106), K562 EVs (2×106) or vehicle (PBS). Neutrophil phagocytic rate (b) and index (c) from SD rats were determined by ink phagocytosis test (* P<0.01 vs. control n = 3). (C): BCR/ABL protein expression of neutrophils in SD rats bearing K562-derived-EVs. SD rats were injected, via tail vein, with K562 cells (2x106) (lane 3), K562-derived-EVs (2×106) (lane 4) or vehicle (PBS) (lane 5). The neutrophils were collected and the expression of BCR/ABL protein was detected by immunoblotting. Samples from HEK293 and K562 cells were taken as negative and positive controls, respectively (lanes 1 and 2). (D): Immune and inflammatory responses of SD rats bearing EVs. SD rats were injected, via tail-vein, with vehicle (PBS), K562-derived-EVs (2×106) or K562 cells (2×106). (a): ratio of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes; (b) plasma CRP (* P>0.05 vs. control, n = 3).