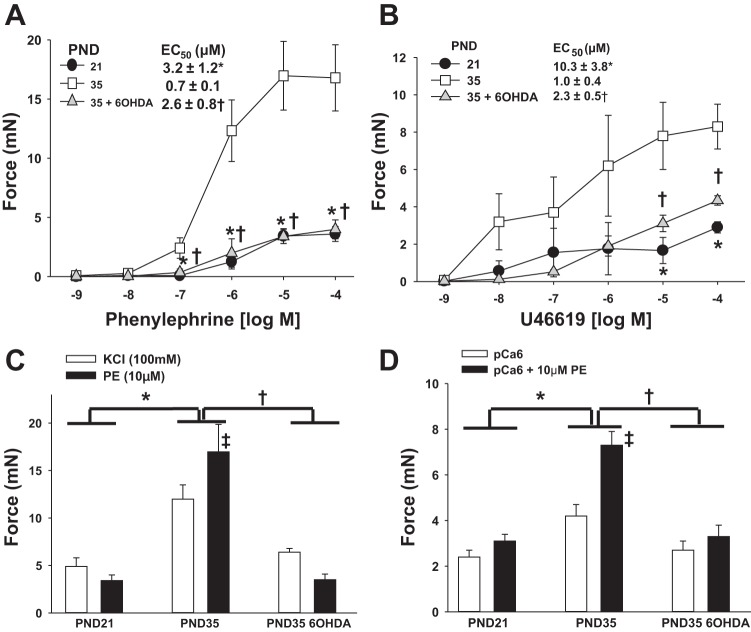
Fig. 5.
Maturation of MA constrictor function and its suppression by chemical sympathectomy. Newborn rats were treated with 6-OHDA to achieve chemical sympathectomy or vehicle and first-order MA (MA1) harvested at PND21 (vehicle) or PND35 (6-OHDA or vehicle). Force generation was measured in intact (A–C) or α-toxin- permeabilized (D) MA1s under isometric conditions in a wire myograph (see materials and methods). Data are plotted as developed force in milliNewtons (mN). A: dose response to the α-adrenergic agonist phenylephrine (PE). B: dose response to the thromboxane mimetic U-46619. C: force generated by KCl-induced depolarization (100 mM) vs. PE (10 μM) (2-way ANOVA). D: force generation in α-toxin-permeabilized MA1s activated with calcium alone (pCa6; 1 μM) or calcium and PE (10 μM) (2-way ANOVA). EC50 was calculated by standard curve analysis. All data are expressed as means ± SE. *P < 0.05, PND35 vehicle vs. PND21; †P < 0.05 PND35 6-OHDA vs. PND35 vehicle. C: ‡P < 0.05 within PND35 (KCl vs. PE activation). D: ‡P < 0.05 within PND35 (pCa6 vs. pCa6 + PE activation). n = 5–6/group.