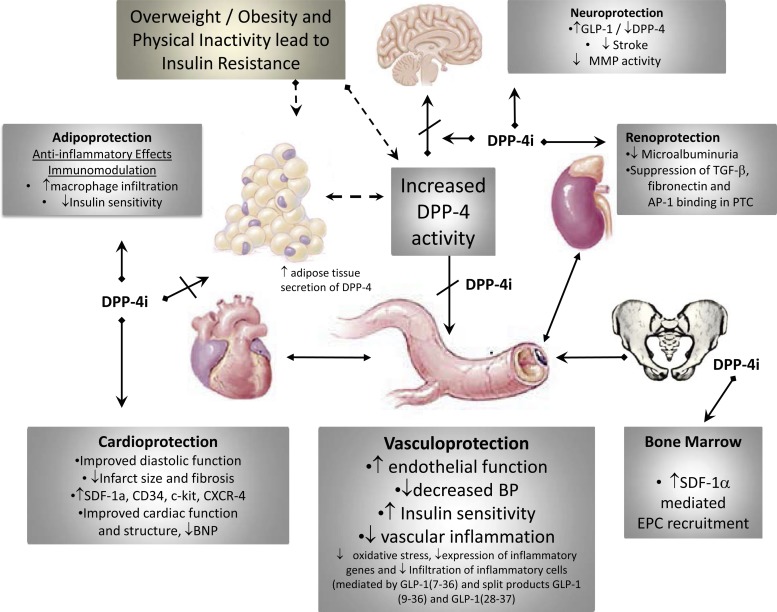
Fig. 1.
Pleiotropic effects of dipeptidylpeptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors (DPP-4i) that benefit the vasculature. DPP-4i exhibit multiple protective effects that collectively contribute to improvement in vascular function which can reduce the risk for development of vascular disease, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. In the setting of obesity/type 2 diabetes mellitus, circulating DPP-4 levels are elevated, due in part to elevated secretion of DPP-4 from inflamed visceral fat. Preclinical and clinical studies examining the efficacy of the DPP-4i have shown improvement in a number of cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes, as indicated in the gray boxes. SDF-1α, stromal cell-derived factor 1α; CXCR-4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; BP, blood pressure; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; AP-1, activator protein-1; PTC, proximal tubule cell; EPC, endothelial progenitor cell.