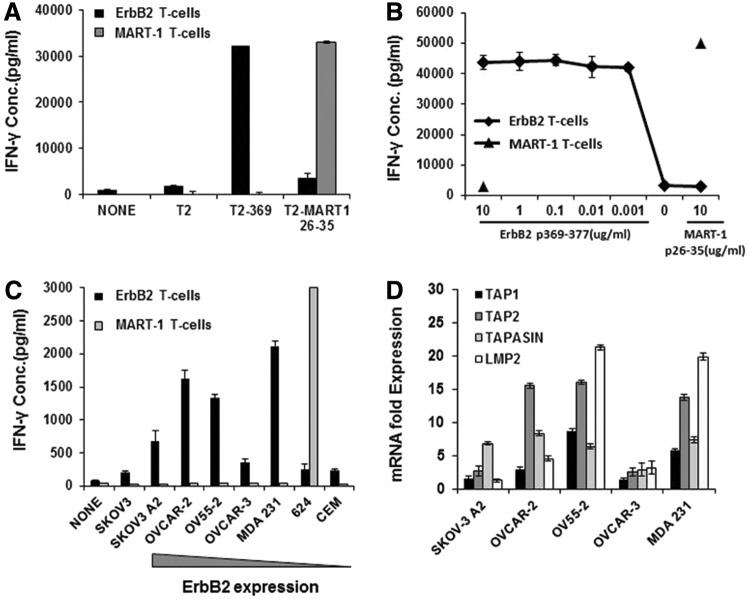
FIG. 2.
ErbB2369–377-specific T cells strongly recognize peptide-pulsed T2 cells and differentially recognize HLA-A2-restricted ErbB2-expressing tumor cells. (A) IFN-γ production of ErbB2369–377-specific T cells in response to peptide-pulsed targets. ErbB2- or MART1-specific T cells were cocultured with T2 cells loaded with HLA-A2-restricted ErbB2369–377 or MART126–35 peptide for 18 hr. (B) ErbB2369–377-specific T cells exhibit high avidity against the relevant peptide. ErbB2369–377-specific T cells were incubated for 18 hr with T2 cells pulsed with a range of concentrations of ErbB2369–377 peptide or 10 ug/mL control (MART-1) peptide. MART1 T cells served as negative control effector T cells. (C) ErbB2 or MART1-specific T cells were cultured alone (none) or stimulated overnight with human HLA-A2-restricted ErbB2+-established cancer cell lines. SKOV-3 (HLA-A2− ErbB2+) and CEM (HLA-A2− ErbB2−) served as negative control tumor targets. (D) APM expression of HLA-A2-restricted ErbB2-expressing tumor cell lines. The mRNA levels of human TAP1, TAP2, TAPASIN, and TAP2 were quantified by real-time PCR. mRNA levels are expressed as fold increase over the APM-negative T2 cell line. β-Actin was used as an endogenous gene control. Results depict the mean±SD of triplicate wells. For all assays, IFN-γ was quantified from cell-free supernatants by ELISA and is reported as the mean concentration (pg/ml)±SEM of duplicate wells. APM, antigen processing machinery; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.