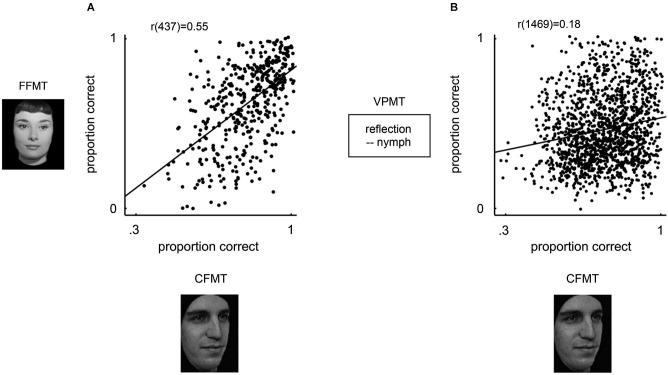
Figure 3.
Specificity of face recognition ability (Wilmer et al., 2012). Face recognition performance (x axis, Cambridge Face Memory Test (CFMT)) is plotted against famous face recognition performance (y axis, graph A, Famous Faces Memory Test (FFMT)) and verbal recognition performance (y axis, graph B, Verbal Paired-associates Memory Test (VPMT)). FFMT and CFMT are very different tests. FFMT measures the ability to name faces stored incidentally in memory over months or years of cultural exposure. CFMT, on the other hand, measures the ability to identify faces stored intentionally in memory shortly before being tested. CFMT and FFMT nevertheless show a high correlation, demonstrating that CFMT captures a general face recognition capacity. CFMT dissociates strongly, however, from VPMT, which measures the ability to identify word-pairs stored intentionally in memory shortly before being tested. This dissociation demonstrates that CFMT captures a specific recognition capacity.