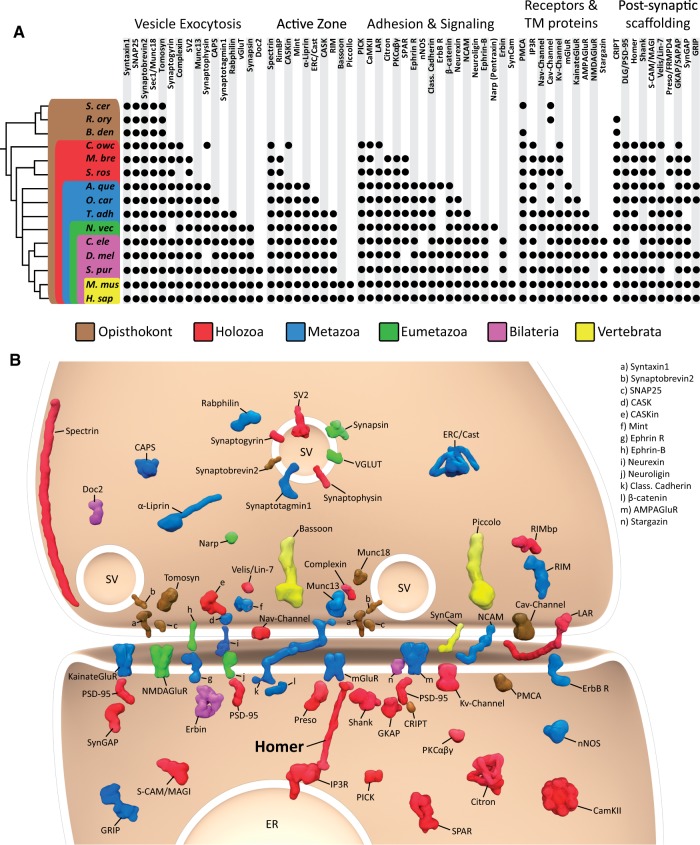
Fig. 1.
The genome of the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta encodes diverse synaptic protein homologs. (A) Metazoan synaptic proteins fall into five major functional categories: Vesicle exocytosis proteins, active zone proteins, adhesion and signaling proteins, receptors and transmembrane (TM) proteins, and postsynaptic scaffolding proteins. A black dot indicates the presence of clear homologs (also see supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online), whereas absence of a dot indicates that a homolog was not detected in that taxon. Taxonomic groupings are indicated as follows: Brown box, Opisthokonta; red box, Holozoa; blue box, Metazoa; green box, Eumetazoa; violet box, Bilateria; yellow box, Vertebrata. The topology of the reference phylogeny was based on a consensus phylogeny (Baldauf 2003; Ruiz-Trillo et al. 2008; Philippe et al. 2009; Fairclough et al. 2013), with the nodes of the earlier branching metazoan lineages collapsed to indicate current controversy concerning their evolutionary relationships. A. que, Amphimedon queenslandica; B. den, Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis; C. ele, Caenorhabditis elegans; C. owc, Capsaspora owczarzaki; D. mel, Drosophila melanogaster; H. sap, Homo sapiens; M. bre, Monosiga brevicollis; M. mus, Mus musculus; N. vec, Nematostella vectensis; O. car, Oscarella carmela; R. ory, Rhizopus oryzae; S. cer, Saccharomyces cerevisae; S. pur, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus; S. ros, Salpingoeca rosetta; T. adh, Trichoplax adhaerens. (B) Graphic representation of an excitatory synapse indicating the subcellular contexts in which many pre- and postsynaptic proteins function. The phylogenetic distribution of each protein is indicated using the color scheme in (A). SV, synaptic vesicle; ER, endoplasmic reticulum.