Fig. 5.
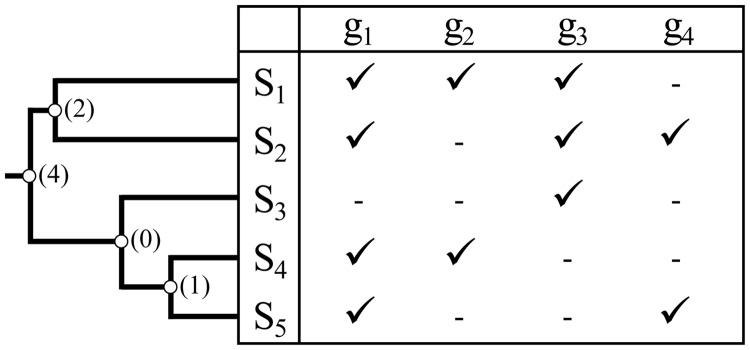
Node data coverage. The data coverage for any node in the phylogenetic tree is the number of genes that directly contribute to the time estimation for that node. A gene is considered to contribute to time estimation for a given node if it has sequences from at least one species pair, one each from the two immediate descendant clades. The figure shows a tree and corresponding data matrix, with genes g1 to g4 and species S1 to S5. Not all genes are available for each species. Available sequences are designated by check marks and missing ones are indicated by dashes in the matrix. Numbers in parentheses next to each node of the tree give the data coverage for that node. We may expect the time estimate for the node with zero data coverage to be very poor, since there is no sequence data to estimate the relevant branch length needed to estimate the divergence time. The best we can say is that it diverged at some time before either of its child nodes but after its parent node.
