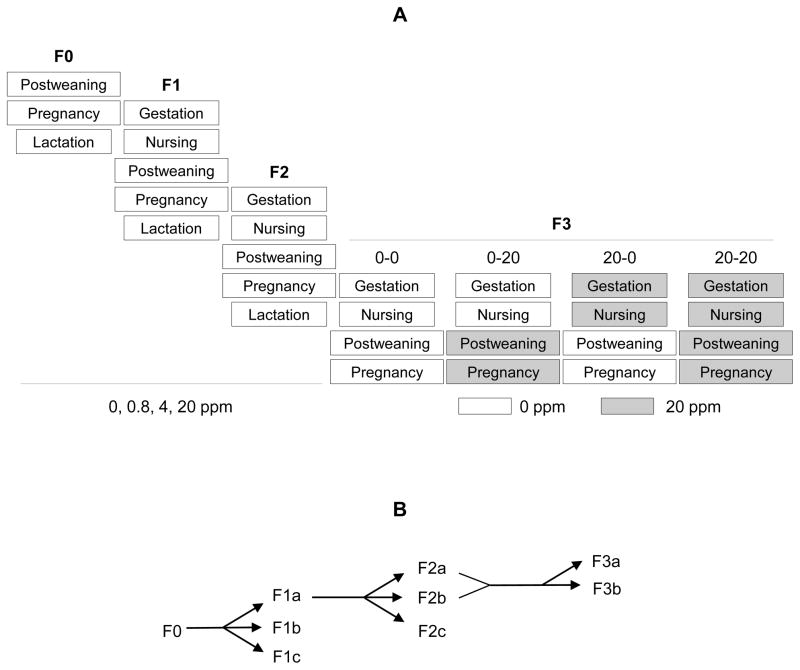
Figure 1.
Treatment and breeding regimens. A. Treatment protocols. F0 generation was treated with 0, 0.8, 4, or 20 ppm ZEA diets during the postweaning period, pregnancy, and lactation; F1 and F2 generations were exposed to 0, 0.8, 4, or 20 ppm ZEA diets during gestation and nursing via maternal exposure and treated with the same ZEA diets during the postweaning period, pregnancy, and lactation via direct dietary exposure. Females in the 0.8 and 4 ppm ZEA-treated F2 generation were dissected on D4.5 without producing F3 generation. In the F3 generation, 0 ppm and 20 ppm ZEA-treated groups were split into two groups each at weaning, and then treated with 0 ppm or 20 ppm ZEA during the postweaning period and pregnancy. B. Breeding regimen. F0 dams produced three litters: F1a, F1b, and F1c; F1a dams produced three litters: F2a, F2b, and F2c; F2a and F2b dams produced two litters: F3a and F3b.