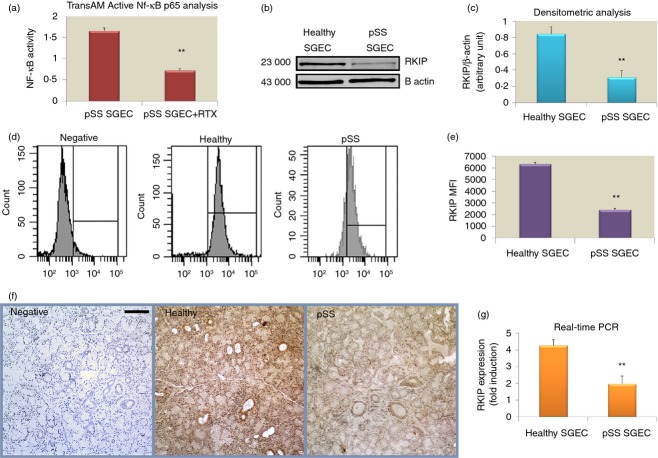
Figure 2.
(a) Rituximab (RTX) treatment decreases nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-DNA-binding activity in primary Sjögren syndrome salivary gland epithelial cells (pSS SGEC). Nuclear fractions were harvested from untreated and RTX-treated pSS SGEC and the binding capacity of p65 NF-κB subunit to a plate-immobilized oligonucleotide containing a κB binding site was measured by TransAM NF-κB assay in the nuclear extracts. Data are means ± SE of three independent experiments. (b, c) Loss of Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) expression in pSS SGEC. Representative Western blot analysis of healthy and pSS SGEC, respectively, showing that the expression levels of RKIP were down-regulated in pSS SGEC. Graph demonstrates the x-fold change in RKIP protein expression compared with β-actin control as measured by densitometry. (d, e) Flow cytometric analysis of RKIP expression in healthy and pSS SGEC. The graph summarizes the results of mean fluorescence intesnity (MFI) evaluation of at least three independent experiments. Data are expressed as mean values ± SE and P-values have been calculated using Student's t-test (**P < 0·01). (f) Representative immunohistochemical staining for RKIP protein on normal healthy minor salivary glands and pSS minor salivary glands. RKIP protein expression was visualized by brown DAB staining. The nuclei were stained with haematoxylin (blue). Scale bar = 20 μm. (g) The endogenous levels of RKIP mRNA in pSS SGEC as measured by real-time quantitative PCR (mean ± SE of three independent experiments; **P < 0·01).