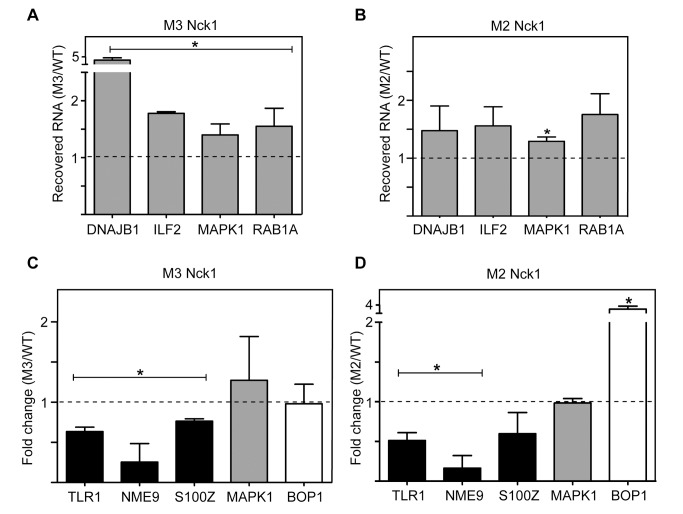
Figure 6. A functional role for Nck1 in cap homeostasis.
Triplicate cultures of U2OS cells were transfected with plasmids expressing HA-tagged wild-type Nck1, Nck1 mutated in the CE-binding domain (M3), or the 5′-kinase-binding domain (M2). Western blots showing overexpression of each of these proteins are in Figure S4. The appearance of uncapped forms of transcripts in the “capping inhibited” pool (grey bars) was determined by their recovery on streptavidin beads after ligation of an RNA adapter and hybridization to a biotinylated antisense DNA oligonucleotide [13]. Each preparation contained an equal amount of uncapped human β-globin mRNA as an internal control and RNA recovered from M3 (A) and M2 (B) expressing cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR for four transcripts that accumulate uncapped forms in cells that are inhibited for cytoplasmic capping (DNAJB1, ILF2, MAPK1, RAB1A). The results are normalized to the signal from cells expressing wild-type Nck1. RNA from M3 (C) or M2 (D) expressing cells was also analyzed by qRT-PCR for three transcripts of the “uninduced” pool whose steady state levels are reduced when cytoplasmic capping is inhibited (TLR1, NME9, S100Z, black bars), one of the transcripts examined in a and b (MAPK1, grey bars), and a control transcript (BOP1, white bars). The results are presented as fold change with respect to wild-type Nck1 and are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The asterisk (*) indicates p<0.05 by Student's unpaired two-tailed t test.